37
1. Turn OFF the gas supply to all other gas-burning ap-
pliances except the furnace.
2. While the furnace is operating, time and record one
complete revolution of the smallest gas meter dial.
3. Calculate the number of seconds per cubic foot (sec/
ft
3
) of gas being delivered to the furnace. If the dial
is a one cubic foot dial, divide the number of sec-
onds recorded in step 2 by one. If the dial is a two
cubic foot dial, divide the number of seconds re-
corded in step 2 by two.
4. Calculate the furnace input in BTUs per hour (BTU/
hr). Input equals the sum of the installation’s gas
heating value and a conversion factor (hours to sec-
onds) divided by the number of seconds per cubic
foot. The measured input must not be greater than
the input indicated on the unit rating plate.
EXAMPLE:
Installation’s gas heating (HTG) value: 1,000 BTU/ft
3
(Obtained from gas supplier)
Installation’s seconds per cubic foot: 34 sec/ ft
3
Conversion Factor (hours to seconds): 3600 sec/hr
Input = (Htg. value x 3600) ÷ seconds per cubic foot
Input = (1,000 BTU/ft
3
x 3600 sec/hr) ÷ 34 sec/ ft
3
Input = 106,000 BTU/hr
NOTE:
The final manifold pressure cannot vary by more than
± 0.3” w.c. for Natural and + 0.5” for LP from the specified
setting. Consult your local gas supplier if additional input rate
adjustment is required.
5. Turn ON gas to and relight all other appliances turned
off in step 1. Be certain that all appliances are func-
tioning properly and that all pilot burners are operat-
ing.
Temperature Rise
Temperature rise must be within the range specified on the
unit rating plate. An incorrect temperature rise may result in
condensing in or overheating of the heat exchanger. An air-
flow and temperature rise table is provided in the Specifica-
tion Sheet applicable to your model. Determine and adjust
temperature rise as follows:
1. Operate furnace with burners firing for approxi-
mately ten minutes. Ensure all registers are open
and all duct dampers are in their final (fully or par-
tially open) position.
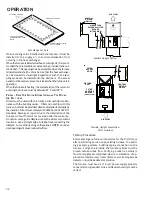
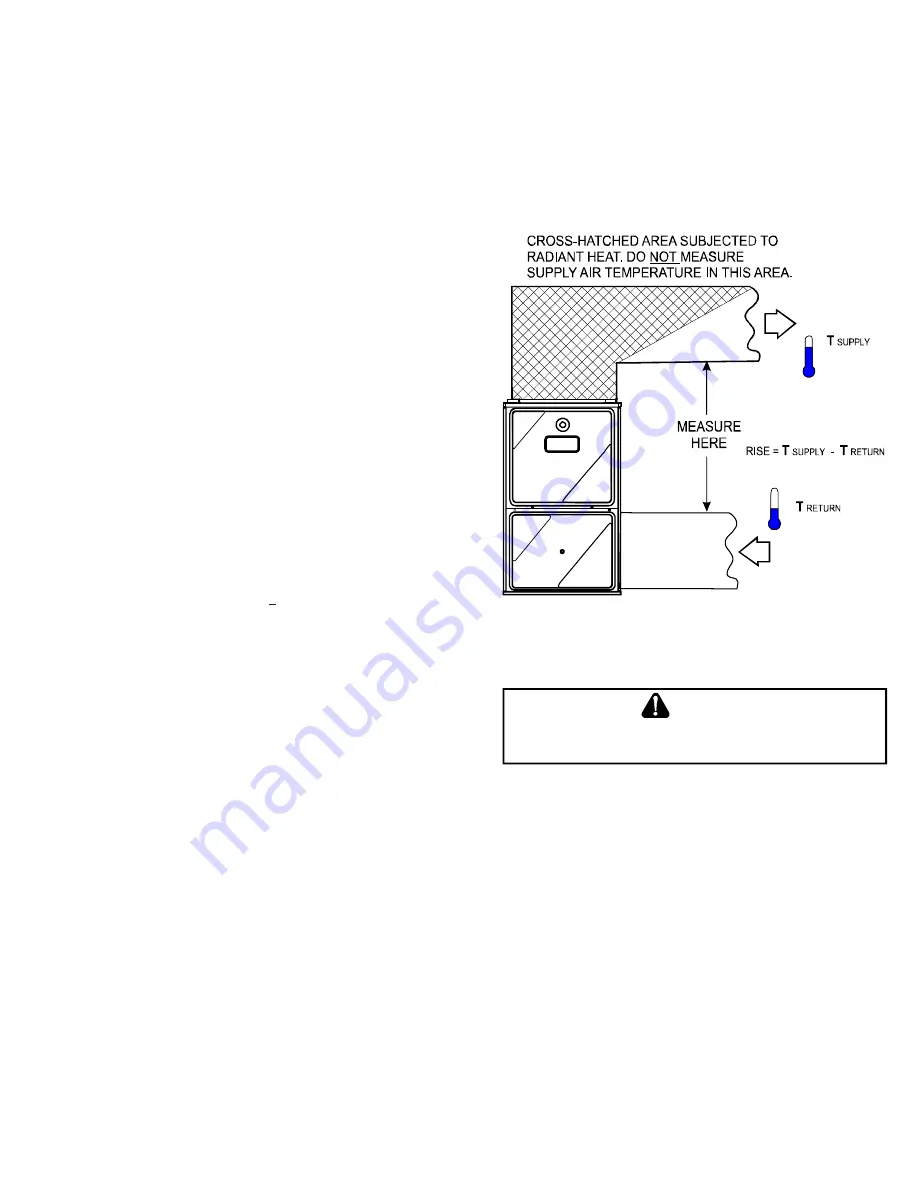
2. Place thermometers in the return and supply ducts as
close to the furnace as possible. Thermometers
must not be influenced by radiant heat by being able
to “see” the heat exchanger.
3. Subtract the return air temperature from the supply
air temperature to determine the air temperature
rise. Allow adequate time for thermometer readings
to stabilize.
4. Adjust temperature rise by adjusting the circulator
blower speed. Increase blower speed to reduce tem-
perature rise. Decrease blower speed to increase
temperature rise. Refer to
Startup Procedure and
Adjustment -Circulator Blower Speeds
for speed
changing details.
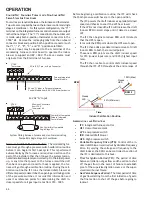
SUPPLY
AIR
RETURN
AIR
Temperature Rise Measurement
C
IRCULATOR
B
LOWER
S
PEEDS
T
O
AVOID
PERSONAL
INJURY
OR
DEATH
DUE
TO
ELECTRICAL
SHOCK
,
TURN
OFF
POWER
TO
THE
FURNACE
BEFORE
CHANGING
SPEED
TAPS
.
WARNING
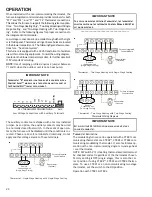
This furnace is equipped with a multi-speed circulator blower.
This blower provides ease in adjusting blower speeds. The
heating blower speed is shipped set at “B”, and the cooling
blower speed is set at “D”. These blower speeds should be
adjusted by the installer to match the installation requirements
so as to provide the correct heating temperature rise and cor-
rect cooling CFM.
Use the dual 7-segment LED display adjacent to the DIP switches
to obtain the approximate airflow quantity. The airflow quan-
tity is displayed as a number on the display, rounded to the
nearest 100 CFM. The display alternates airflow delivery indi-
cation and the operating mode indication.
Example:
The airflow being delivered is 1225 CFM. The dis-
play indicates 12. If the airflow being delivered is 1275, the
display indicates 13.
OPERATION