5
space, the number of windows and ventilation openings, the
number of doors to the outside, internal doors which can close off
unconfined space, and overall tightness of building construction.
Consideration must also be given to the amount of storage items
(furniture, boxes, etc.) within the unconfined space which take
away from the air volume. (Refer to Table 2.)
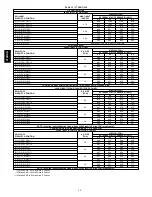
Table 2 – Minimum Floor Area For Unconfined Space
FURNACE
INPUT BTUH / kW
MINIMUM FT
2
(M
2
) WITH
7---1/2 FT (2.3 M) CEILING
70,000
467 (43.4)
91,000
607 (56.3)
105,000
700 (65.0)
119,000
793 (73.6)
140,000
933 (86.6)
154,000
1026 (95.3)
Many new buildings and homes (and older ones that have been
weatherized) MUST BE considered as being of tight construction,
therefore infiltration will not be sufficient to supply necessary air
for combustion and ventilation.
A building can be considered as being of tight construction when:
1. Walls and ceilings exposed to outside atmosphere have a
continuous water vapor retarder with a rating of 1 perm or
less with openings gasketed or sealed; and/or
2. Weatherstripping has been added on operable windows and
doors, and/or caulking or sealants are applied to areas such
as joints around windows and door frames; between sole
plates and floors; between wall--ceiling joints; between wall
panels; at penetrations for plumbing, electrical, and fuel
lines; and at other openings.
If combustion and ventilation air must be supplied to an
unconfined space from outside, an opening with a FREE AREA of
not less than 1 in.
2
per 5,000 BTUH (4400 mm
2
/ kW)of total
input of all appliances within unconfined space (but not less than
100 in.
2
(64516 mm
2
) must be provided. This opening must be
located such that it cannot be blocked at any time.
Confined Space
A confined space has a volume of less than 50 ft
3
(1.4 M
3
) per
1,000 BTUH of the total input rating for all appliances installed in
that space.
NOTE
: In calculating free area, consideration shall be given to
blocking effect of louvers, grilles, or screens protecting openings.
Screens used shall not be smaller than 1/4--in. (6 mm) mesh and
shall be readily accessible for cleaning. If free area through a louver
or grille is known, it shall be used in calculating size and free area
specified. If design and free area are not known, it may be assumed
that wood louvers have 20% free area and metal louvers and grilles
have 60% free area. Louvers shall be fixed in open position or
interlocked with furnace so they open automatically at furnace
start--up and remain open during furnace operation.
The size of the openings depends upon whether the air comes from
outside of the structure or an unconfined space inside the structure.
All Air From Inside the Structure
For a confined space, where air is taken from an interior space, 2
permanent openings of equal area are required. One opening must
be within 12 in. (305 mm) of ceiling and the other within 12 in.
(305 mm) of floor.
All Air From Outside of Structure
If outside air is supplied to a confined space, then the 2 openings
must be equal and located as above.
1. If combustion air is taken through a permanent opening
directly communicating with the outdoors, the opening shall
have a minimum free area of 1 in.
2
per 4,000 BTUH (550
mm
2
/kW)of total input rating for all equipment in the
enclosure.
2. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through vertical
ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at least 1 in.
2
of
free area per 4,000 BTUH of the total input for all
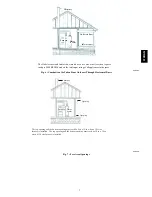
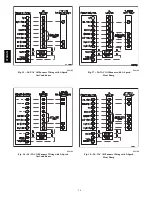
equipment within the confined space. (See Fig. 4 and 5.)
3. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through horizontal
ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at least 1 in.
2
of
free area per 2,000 BTUH (1100 mm
2
/kW)of the total input
for all equipment within the confined space. (See Fig. 6.)
When ducts are used to supply air, they must be of the same cross
sectional area as free area of openings to which they connect. (See
Fig. 7.)
The minimum dimension of rectangular air ducts must not be less
than 3 in. (76 mm).
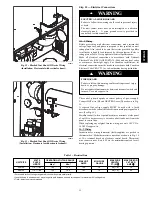
Step 3 — Ductwork Recommendations
CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal injury
or death.
When supply ducts carry air circulated by furnace to areas
outside spaces containing furnace, return air MUST also be
handled by a duct sealed to furnace casing and terminating
outside space containing furnace.
!
WARNING
UNIT MAY NOT OPERATE
Failure to follow this caution may result in intermittent unit
operation.
Return--air grilles and warm air registers MUST NOT be
obstructed.
CAUTION
!
The proper sizing of warm air ducts is necessary to ensure
satisfactory furnace operation. Ductwork should be in accordance
with the latest editions of NFPA--90A (Installation of Air
Conditioning and Ventilating Systems) and NFPA--90B (Warm Air
Heating and Air Conditioning Systems) or Canadian equivalent.
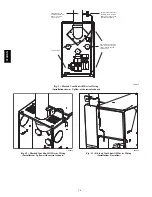
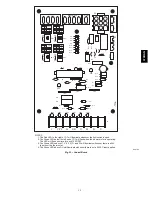
The supply ductwork should be attached to flanged front opening
provided at discharge end of furnace. The return--air ductwork
should be attached to flanged rear opening of furnace. See Fig. 2
for dimensions of these openings.
NOTE
: The blower access opening should not be used for return
air.
The following recommendations should be followed when
installing ductwork:
1. Install locking--type dampers in all branches of individual
ducts to balance out system. Dampers should be adjusted to
impose proper static at outlet of furnace.
2. A flexible duct connector of noncombustible material
should be installed at unit on both supply-- and return--air
systems. In applications where extremely quiet operation is
necessary, the first 10 ft. (3.0 M) (if possible) of supply and
return ducts should be internally lined with acoustical
material.
3. In cases where return--air grille is located close to fan inlet,
there should be at least one 90
_
air turn between fan inlet
and grille. Further reduction in sound level can be
accomplished by installing acoustical air--turning vanes or
lining duct as described in item 2 above.
4. When a single air grille is used, duct between grille and
furnace must be the same size as return opening in furnace.
374RAN