93
ATmega103(L)
0945G–09/01
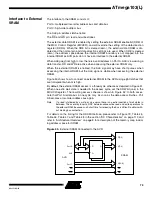
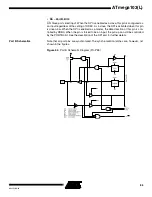
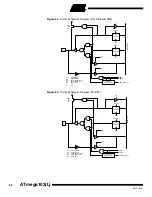
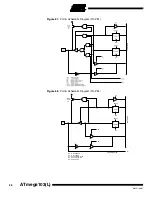
Figure 65.
Port D Schematic Diagram (Pins PD6 and PD7)
Port E
Port E is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors.
Three I/O memory address locations are allocated for the Port E, one each for the Data
Register – PORTE, $03($23), Data Direction Register – DDRE, $02($22) and the Port E
Input Pins – PINE, $01($21). The Port E Input Pins address is read-only, while the Data
Register and the Data Direction Register are read/write.
The Port E output buffers can sink 20 mA. As inputs, Port E pins that are externally
pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated.
All Port E pins have alternate functions as shown in Table 33.
When the pins are used for the alternate function, the DDRE and PORTE registers have
to be set according to the alternate function description.
DA
T
A
BUS
D
D
Q
Q
RESET
RESET
C
C
WD
WP
RD
MOS
PULL-
UP
PDn
R
R
WP:
WD:
RL:
RP:
RD:
n:
m:
WRITE PORTD
WRITE DDRD
READ PORTD LATCH
READ PORTD PIN
READ DDRD
6, 7
1, 2
DDDn
PORTDn
SENSE CONTROL
TIMERm CLOCK
SOURCE MUX
CSm2
CSm0
RL
RP
CSm1
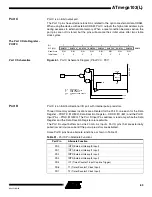
Table 33.
Port E Pin Alternate Functions
Port Pin
Alternate Function
PE0
PDI/RXD (Programming Data Input or UART Receive Pin)
PE1
PDO/TXD (Programming Data Output or UART Transmit Pin)
PE2
AC+ (Analog Comparator Positive Input)
PE3
AC- (Analog Comparator Negative Input)
PE4
INT4 (External Interrupt4 Input)
PE5
INT5 (External Interrupt5 Input)
PE6
INT6 (External Interrupt6 Input)
PE7
INT7 (External Interrupt7 Input)