106
ATmega103(L)
0945G–09/01
Bit 1 = SUT1 Fuse bit
Bit 0 = SUT0 Fuse bit
Bit 7, 6, 4, 2 = “1”. These bits are reserved and should be left unprogrammed (“1”).
3.
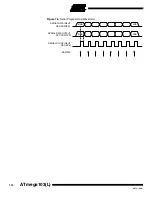
Give WR a
t
WLWH_PFB
wide negative pulse to execute the programming.
t
WLWH_PFB
is found in Table 41. Programming the Fuse bits does not generate any activity
on the RDY/BSY pin.
Programming the Lock Bits
The algorithm for programming the Lock bits is as follows (refer to “Programming the
Flash” on page 102 for details on command and data loading):
1.
A: Load Command “0010 0000”.
2.
D: Load Data Low Byte. Bit n = “0” programs the Lock bit.
Bit 2 = Lock Bit2
Bit 1 = Lock Bit1
Bit 7 - 3, 0 = “1”. These bits are reserved and should be left unprogrammed (“1”).
3.
L: Write Data Low Byte.
The Lock bits can only be cleared by executing Chip Erase.
Reading the Fuse and Lock
Bits
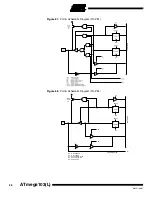
The algorithm for reading the Fuse and Lock bits is as follows (refer to “Programming
the Flash” on page 102 for details on command loading):
1.
A: Load Command “0000 0100”.
2.
Set OE to “0”, and BS to “0”. The status of the Fuse bits can now be read at
DATA (“0” means programmed).
Bit 5 = SPIEN Fuse bit
Bit 3 = EESAVE Fuse bit
Bit 1 = SUT1 Fuse bit
Bit 0 = SUT0 Fuse bit
Set OE to “0”, and BS to “1”. The status of the Lock bits can now be read at DATA
(“0” means programmed).
Bit 2 = Lock Bit2
Bit 1 = Lock Bit1
3.
Set OE to “1”.
Reading the Signature Bytes
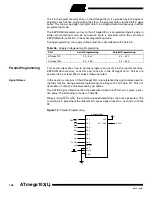
The algorithm for reading the signature bytes is as follows (refer to “Programming the
Flash” on page 102 for details on command and address loading):
1.
A: Load Command “0000 1000”.
2.
C: Load Address Low Byte ($00 - $02).
Set OE to “0”, and BS to “0”. The selected signature byte can now be read at DATA.
3.
Set OE to “1”.