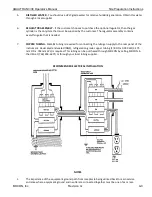
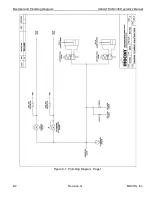
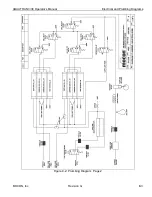
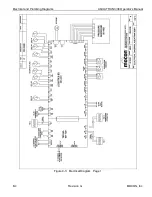
Theory of Operation
AQUATRAN 3/38 Operator’s Manual
D-2
Revision G
MOCON, Inc.
Room temperature and humidity are just two of many factors that can marginally affect test results.
Consequently, a piece of film with a known WVTR will test higher or lower.
Any reference film, whose WVTR has been established, may be used for calibration. A reference film at any
arbitrarily constant test flow will produce an arbitrary constant amount of water vapor in the carrier gas. The
infrared sensor/amplifier produces a DC output proportional to the amount of water vapor. The DC output is
converted to a value and transmitted to the computer.
The computer subtracts the ReZero value from the DC output value. The result is converted to units of
Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) using a scaling factor determined by the nitrogen gas flow rate.
Factors that Affect the Transmission Rate of a Barrier Material
The water vapor transmission rate of barrier materials is affected by several factors:
•
Barrier test temperature
•
Test Gas (water vapor) concentration effect on driving force
•
Barometric pressure effect on measured transmission rate
•
Relative humidity
Barrier Temperature
The temperature at which the barrier is tested has a great effect (usually logarithmic) on transmission rate.
This makes temperature one of the most important test conditions for most barrier materials. Many barriers
exhibit a 6% to 15% rise in water vapor transmission rate for each degree C rise in temperature.