60
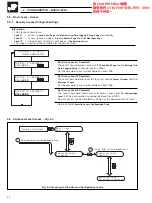
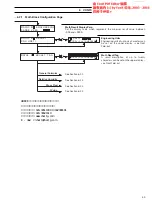
MATHS M INPUT a
SOURCE ANLG I/P
MATHS M
MATHS M INPUT a
CONSTANT
MATHS M INPUT b
TYPE
MATHS M INPUT b
SOURCE
MATHS M INPUT b
CONSTANT
MATHS M INPUT c
TYPE
MATHS M INPUT c
SOURCE
MATHS M INPUT c
CONSTANT
Variable
Constant
Variable
MATHS M INPUT a
TYPE VARIABLE
CONSTANT
Constant
MATHS M INPUT a
DEC POINT
MATHS M INPUT b
DEC POINT
MATHS M INPUT c
DEC POINT
BLOCK TO CONFIGURE
M
Constant
…6
CONFIGURATION – ADVANCED LEVEL
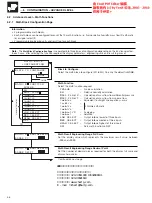
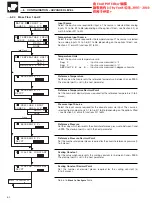
Input Type
Select the input type required for input a:
VARIABLE
–
Input signal (analog input or math block)
CONSTANT
–
Arithmetic value used as multiplier, divisor or for addition or
subtraction
Input Source
Select the input source required for input a. The source is selected from analog
inputs A1 to A6, B1 to B6 (depending on the options fitted – see Section 4.2) or
math functions M1 to M4.
Input Constant Value
Set an arithmetic value between the values –999 and +9999.
Input Constant Decimal Point
Set the number of decimal places for the input (0 to 3 places).
Input b
Select the type, source or constant as required for input b. The method is as for
input a.
Input c
Select the type, source or constant as required for input c. The method is as for
input a.
Return to
Block to Configure
frame.
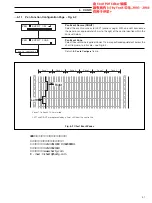
6.2.2
General Formulæ
These functions referred to as general formulæ are as follows:
(a x b) + c
(a – b)
c
(a + b)
c
(a x b)
c
3
(a + b + c)
LOW SELECT
MED SELECT
HIGH SELECT
(a + b + c)
In each of these functions the three inputs can be configured as variables or constants. A variable uses an input source, either analog
or another math function.