MANUAL MOTOR STARTER GUIDE
APRIL 19
67/80
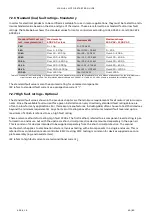
7.6.1.1 Manual starters (non-combination)
Manual starting methods offer a cost-effective alternative to remotely controlled starters. Manual starters feature a
front-facing switching mechanism, typically in the form of a rotary knob, toggle switch, or pushbutton. This mecha-
nism is the interface for direct ON/OFF control of the load. What sets manual motor starters apart from simple
motor switches (e.g. non-fusible disconnect switches) is the inclusion of protective releases. If a fault occurs, the
switching mechanism will trip the device handle to either an OFF or designated TRIP position.
As these manual starters still require that additional branch protection be provided separately upstream, they are
commonly identified using the terms “non-combination” or “non-combo”.
Manual starters are often used on smaller 1- or 3-phase motors, typically 10 hp or less, and are popular in HVAC appli-
cations. They can either be enclosed or provided with accessories for flush mounting directly to a wall or panel door.
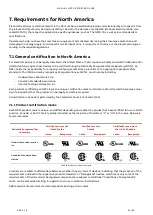
The examples in the figure below show manual motor starters applied as non-combination, single-motor starters. In
addition to providing the means for motor control and overload protection, they can be used as the main branch dis-
connect when marked “Suitable as Motor Disconnect” and installed on the load side of the branch circuit protective
device.
Manual motor starters as non-combination manual starters
Branch functional requirements
Disconnect means
Disconnect means (alternate)
Short-circuit and ground-fault protection
Control means
Overload protection
Application information
Starting method: Manual
SCCR reference for MMS: “Motor Disconnect”
Maximum voltage: 600
Δ
Upstream branch protection: Required
Figure 38: Manual motor starters as non-combination manual starters.
For information regarding the use of manual motor starters as manual self-protected Combination Motor Controllers
(Type E), witho
ut the need for upstream branch circuit protection, see Chapter 7.6.2 Defining Combination Motor Con-