1.1 Outline
1-2
1.1 Outline
EtherCAT is a real-time field bus, based on the IEEE802.3 standard Ethernet, which was advocated by Beckhoff Auto-
mation GmbH. Currently it is being standardized as IEC61185 Type 12 of the IEC (International Electrotechnical Com-
mission).
The spread of EtherCAT is advancing with the focus on Europe, and it is applied to press machines, injection molding
machines, CNC units, robots, and so on. ETG (EtherCAT Technology Group) is also working to increase the spread of
EtherCAT.
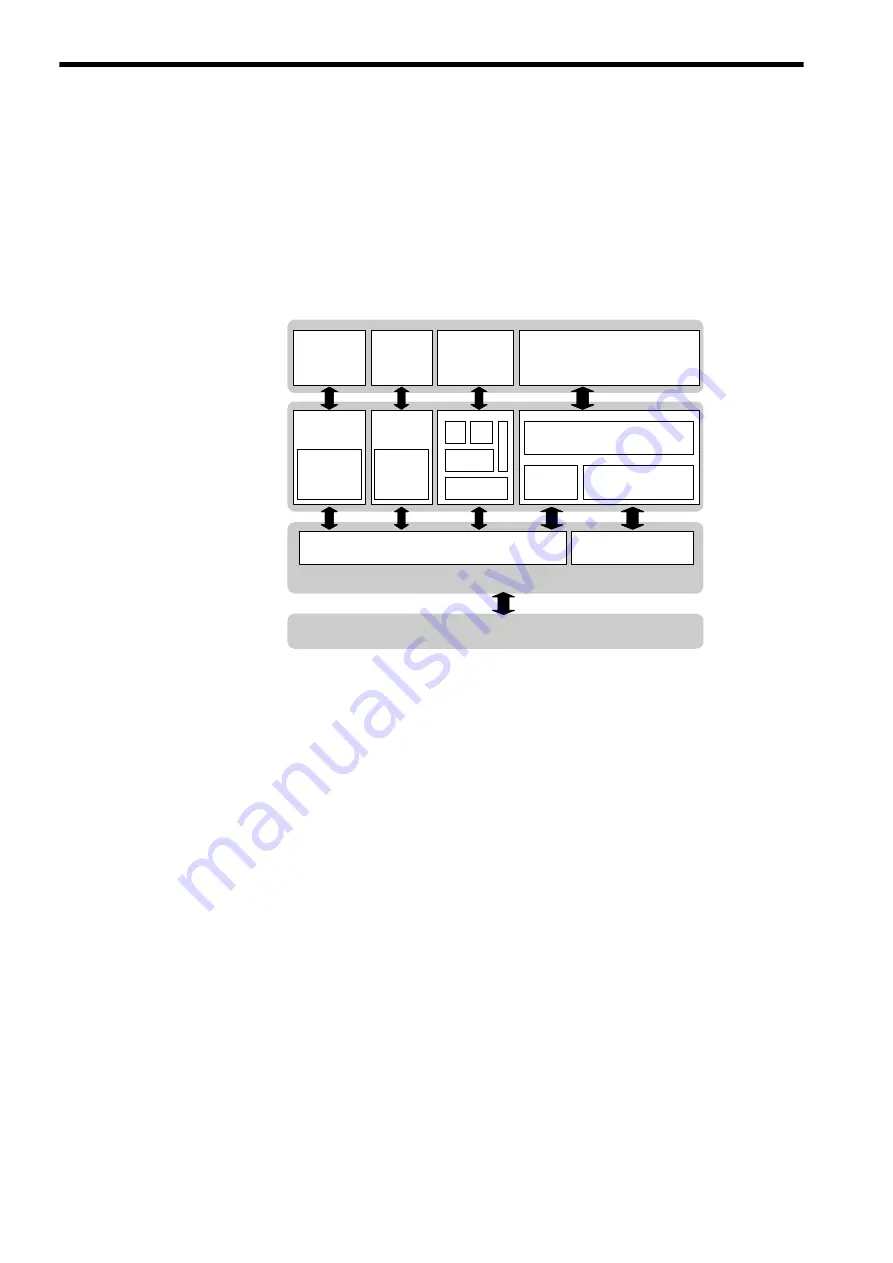
An EtherCAT device model (ISO/OSI reference) is shown below.
1.2 Features
The features of EtherCAT are listed below.
• Since Ethernet (ISO/IEC8802-3) is used in the physical layer, it is possible to use general-purpose Ethernet
cables.
• Ethernet frames are transmitted to the next node in a high-speed repeat system, enabling high-efficiency commu-
nication.
∗
This is the transmission cycle (guide) based on EtherCAT specifications. Some lag occurs in the actual data
refresh cycle in accordance with the communication cycle of the master device and the data refresh cycle of
the slave devices.
• Synchronization with jitter of no greater than 1 ms is possible with a clock synchronization system conforming to
IEEE1588.
• Unrestricted network topology (line type, star type, tree type, and daisy-chain type connections are possible.)
Servo
amplifier
application
(IEC 61491)
Application
HTTP,
FTP, ...
Application
(e.g.: DS402 drive profile)
SoE
service
channel
File
access
TCP UDP
IP
Ethernet
Object dictionary
SDO
PDO mapping
Mailbox
EtherCAT slave controller
Process data
Ethernet physical layer
Application
layer
Data link
layer
Physical
layer
At 100 Mbps in the full duplex mode*:
(reference data)
Band usage ratio: 80 to 90%
Data update time
Reading/writing 256 digital I/O points:
11
μ
s
Reading/writing 1,000 digital I/O points at 100 nodes:
30
μ
s
Reading/writing analog I/Os (16-bit, 20 kHz) at 200 nodes: 50
μ
s
Reading/writing servo axes (8-byte) at 100 nodes:
100
μ
s
Reading/writing 12,000 digital I/O points:
350
μ
s















































