66 Mounting
WAGO-I/O-SYSTEM 750
750-325 CC-Link Fieldbus Coupler
Manual
Version 2.0.1
5.6.3
Inserting the I/O Module
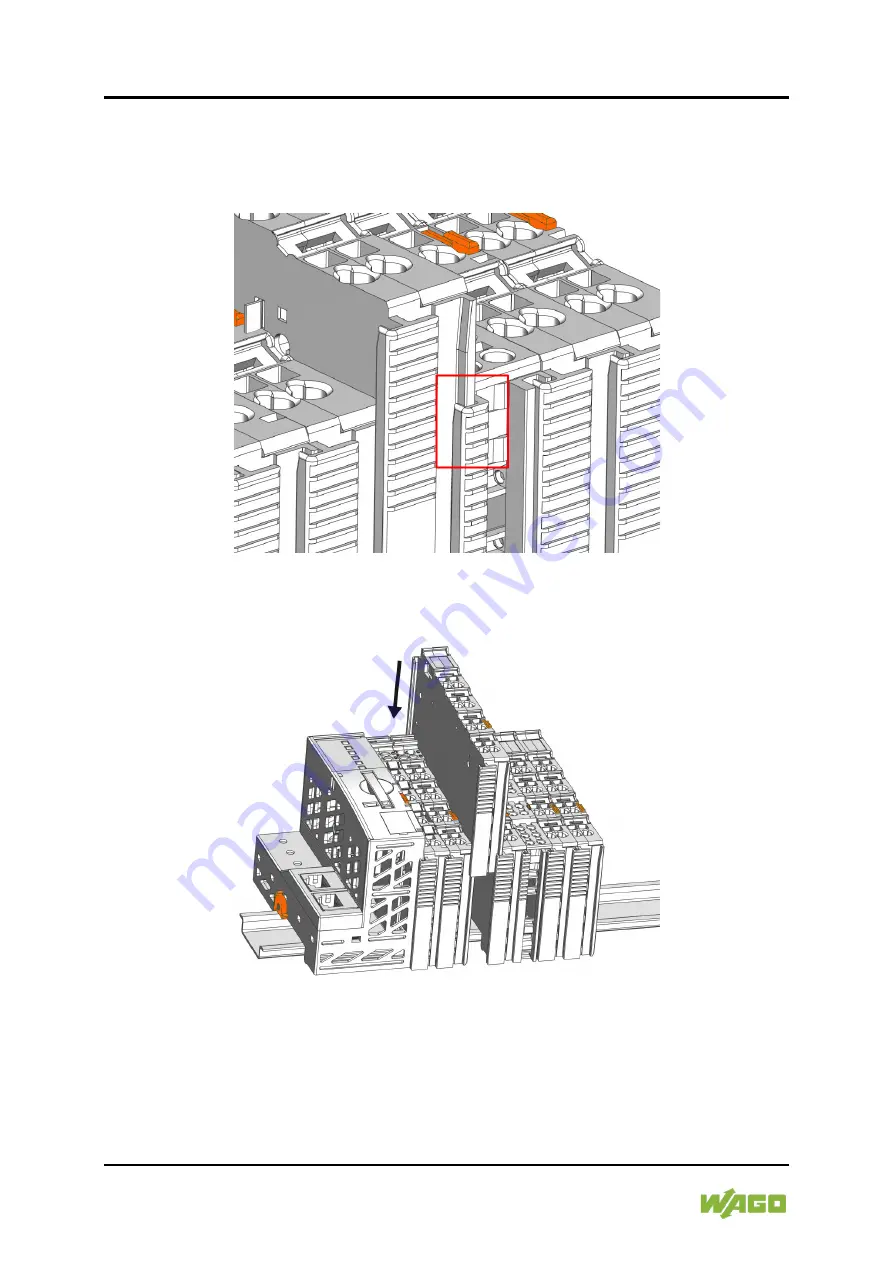
1.
Position the I/O module in such a way that the groove and spring are
connected to the preceding and following components.
Figure 33: Inserting I/O Module (Example)
2.
Press the I/O module into the assembly until the I/O module snaps into the
carrier rail.
Figure 34: Snap the I/O Module into Place (Example)
3.
Check that the I/O module is seated securely on the carrier rail and in the
assembly. The I/O module must not be inserted crooked or askew.
Once the I/O module has snapped into place, the electrical connections for the
data contacts and power contacts (if any) to the head station or to the preceding
and, if applicable, following I/O module are established.
















































