The first step in the process is to gain layer-1 interoperability between chipset vendors. Once that is
achieved, system vendors can perform additional tests between CPE and DSLAMs. The DSL Forum is
defining the framework for the VDSL2 tests in several important documents that will guide the industry
forward.
For the reasons stated, above, the BX100V is equipped with different vendor profiles to deal with potential
compatibility issues and customer deployments.
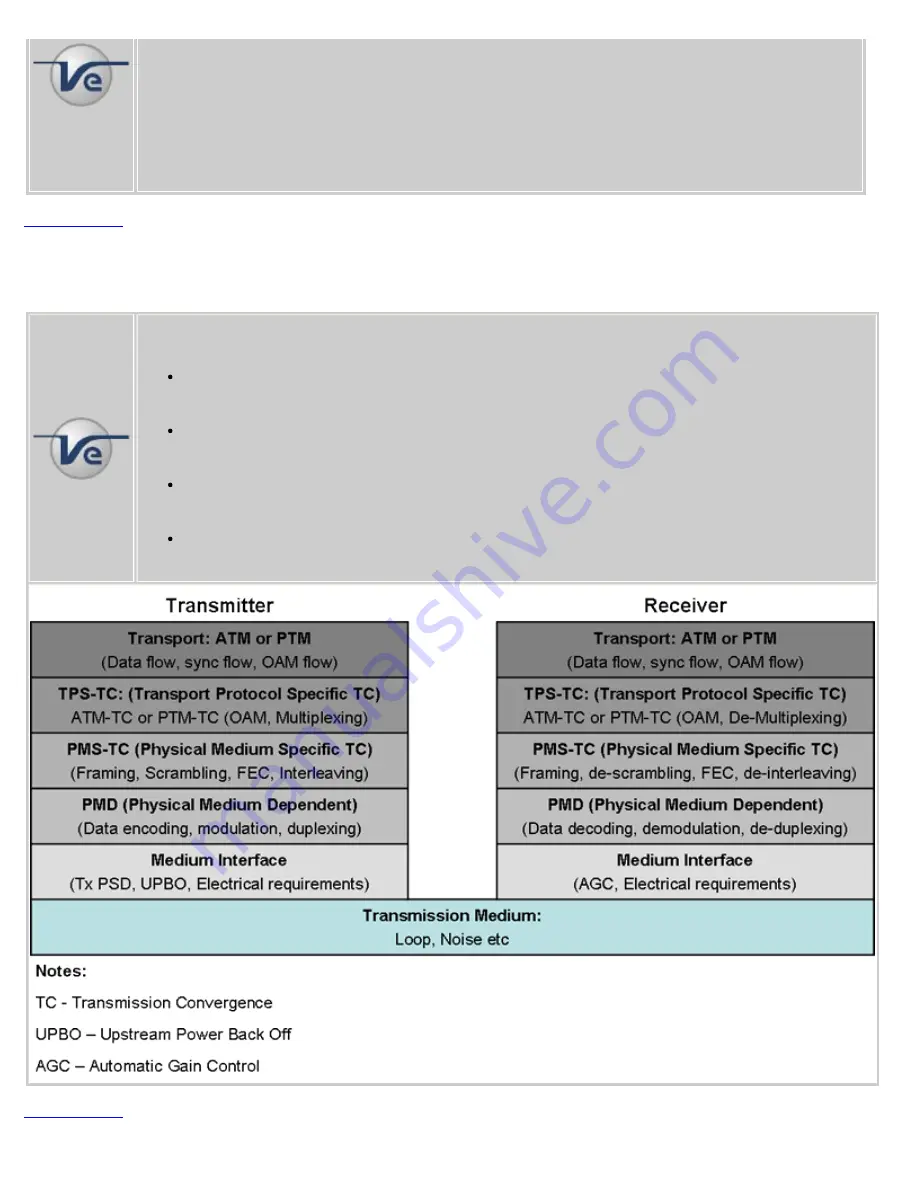
ATM mode
: Enables Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) encapsulation of Ethernet frames.
PTM mode:
Enables Packet Transfer Mode (PTM) encapsulation of Ethernet frames.
Note:
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) versus Packet Transfer Mode (PTM)
VDSL2 specifies a Packet Transfer Mode – Transmission Convergence (PTM-TC) function that is based
on the Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) IEEE 802.3ah standard. The PTM-TC specified in VDSL2
makes provision for Preemption and Short Packet Support.
Preemption improves traffic management by pausing the transmission of a low-priority packet when a
high-priority packet needs to be transmitted. Thus high-priority packets (e.g. voice) experience a
minimum amount of packet insertion delay.
Short Packet Support enables a VDSL2 system to transport packets that contain less than 64 bytes.
While IEEE802.3 was designed exclusively for the transport of Ethernet packets greater than 64 bytes,
VDSL2 transports any packet type, including IP packets which are often less than 64 bytes.
So when introducing VDSL2, there will be a strong tendency from operators to drop ATM in the first
mile, and to replace it with Ethernet (64/65 encapsulation).
BX100A/V e-Manual D07-00-001 Rev E01
Page 17 of 52
















































