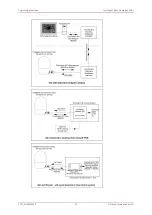
Intelligent Gyro Compass (iGC)
0707-SOM-00004-7
14
© Tritech International Ltd.
4. Installation
4.1. Safety Note
Before commencing installation of the iGC:
1. Refer to Chapter 1,
2. All relevant parts of this section of the manual should be read and understood
4.2. iGC Mechanical Installation
4.2.1. Introduction
When deciding where to mount the iGC, consideration should be given to:
1. Its location relative to magnetically active materials on the host system
2. Alignment with the axes of the host system
3. Stiffness of the mounting arrangement
4. Collision protection
4.2.2. Magnetic Disturbance
To reduce the effects of fixed magnetic disturbances on the iGC output, it should be mounted
as far as is practically possible from the following:
1. Ferrous or other magnetically active materials (including fasteners or brackets used to
mount the iGC)
2. Sources of electrically induced magnetic fields such as motors and transformers
3. Moving equipment (e.g. manipulator arms, pan & tilt units etc.)
The iGC is more susceptible to ferrous materials underneath the assembly than from the
side or above.
4.2.3. Alignment
The electrical connector is mounted at the “rear” of the iGC. In addition, three meridian lines
have been engraved into the body of the iGC. These show the forward, port and starboard
directions of the iGC axes. (Refer to Section 4.3, “ Installation Drawing ” for details).
To maximise the accuracy of the iGC outputs, its pitch, roll and yaw axes should be aligned,
as accurately as possible, with the pitch, roll and yaw axes of the host system / vehicle.
If necessary, small corrections can be made in accordance with the commissioning and
calibration sections of this manual, provided that the existing host control system can provide
this function, or the iGC is being used with the iGC PC software, iFG or iIF.