6-7
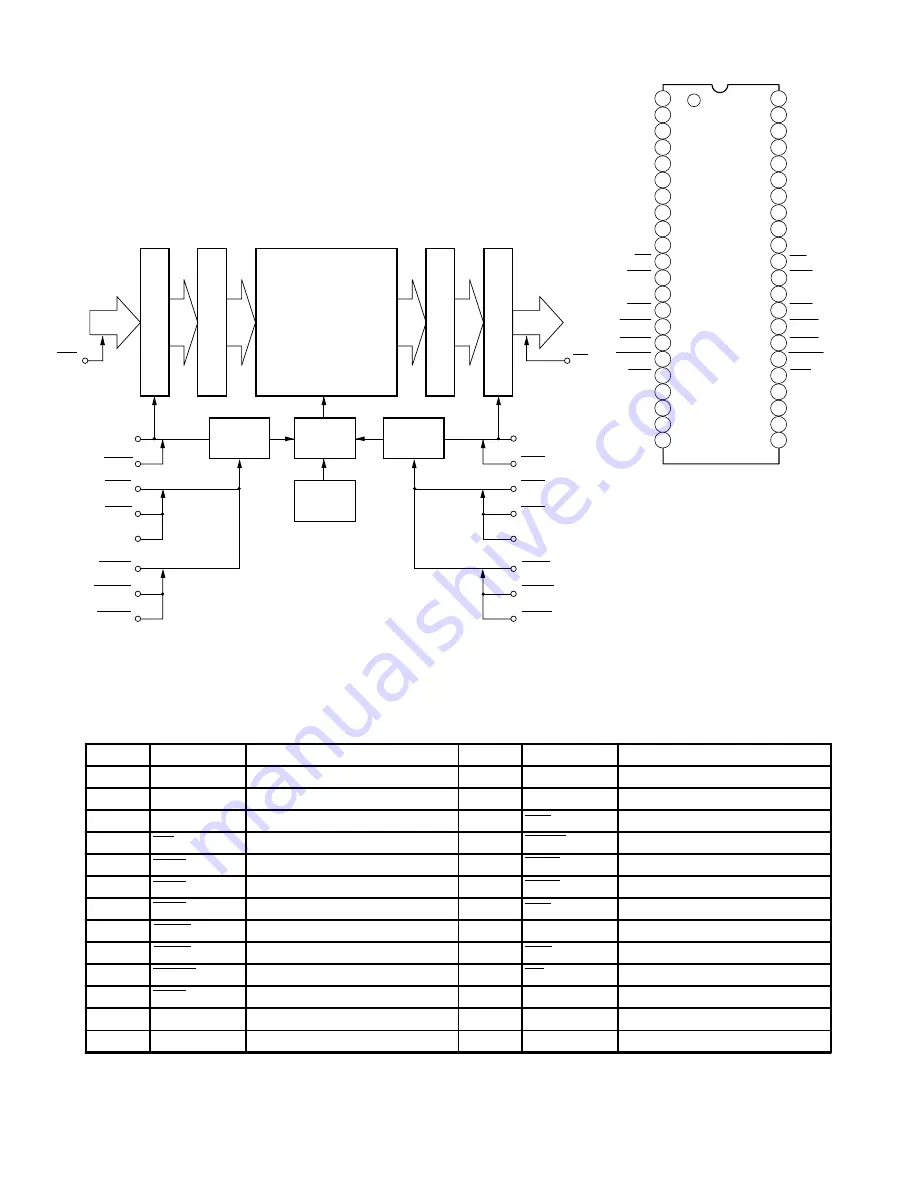
Fig. 6-8 HM530281RTT-20 internal block diagram
2-3. Memory
HM530281RTT-20 (QX19, QX20, QX21) is a 2.5 Mbit
field memory. The pin configuration of the IC is shown in
Fig. 6-7 , terminal function in table 6-2 and internal block
diagram in Fig. 6-8.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
Din 0
Din 1
Din 2
Din 3
Din 4
Din 5
Din 6
Din 7
Vss
Vcc
WE
CGW
WCK
WRS
WLRS
WCLR
WWND
WAS
WAD
MODE 0
MODE 1
TEST
Dout 0
Dout 1
Dout 2
Dout 3
Dout 4
Dout 5
Dout 6
Dout 7
Vss
Vcc
OE
CGR
RCK
RRS
RLRS
RCLR
RWND
RAS
RAD
TEST 1
TEST 2
TEST 3
33
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
Fig. 6-7 HM530281RTT-20
pin function
32-word
x 8
32-word
x 8
32-word
x 8
32-word
x 8
Write data register
Write data buffer
Read data buffer
Read data register
x 8
x 8
D in
D out
WE
OE
Memory array
1152 dot x 288 line x 8*
1
1024 dot x 324 line x 8*
1
10368 dot x 32 word x 8*
1
WCK
CGW
WRS
WAS
WAD
WLRS
WWND
WCLR
RCK
CGR
RRS
RAS
RAD
RLRS
RWND
RCLR
Write
counter
Read
counter
Memory
controller
Refresh
counter
Note : 1. Selected by the mode pin
Table 6-2 HM530281RTT-20 pin configuration
Pin No.
Name
Function
Pin No.
Name
Functions
1 - 8
D
IN0 - 7
Data input
22 - 25
TEST 0 - 3
Connect to GND.
9
V
SS
GND
26
RAD
Read address
10
V
CC
Power supply voltage
27
RAS
Read address set
11
WE
Write enable
28
RWND
Read window mode
12
CGW
Write clock gate
29
RCLR
Read clear
13
WCK
Write clock
30
RLRS
Read line reset
14
WRS
Write reset
31
RRS
Read reset
15
WLRS
Write line reset
32
RCK
Read clock
16
WCLR
Write clear
33
CGR
Read clock gate
17
WWND
Write window mode
34
OE
Output enable
18
WAS
Write address set
35
V
CC
Power supply voltage
19
WAD
Write address
36
V
SS
GND
20 - 21
MODE 0 - 1
Mode selection input
37 - 44
D
OUT0 - 7
Data output
Summary of Contents for TLP411E
Page 1: ...FIE NO 336 9612 Dec 1996 TECHNICAL TRAINING MANUAL 3 LCD DATA PROJECTOR TLP411U TLP411E ...
Page 4: ...1 1 SECTION I MAIN POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT ...
Page 10: ...2 1 SECTION II LAMP HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT ...
Page 12: ...3 1 SECTION III OPTICAL SYSTEM ...
Page 16: ...4 1 SECTION IV RGB DRIVE CIRCUIT ...
Page 25: ...5 1 SECTION V MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 39: ...6 1 SECTION VI DIGITAL CIRCUIT ...
Page 63: ...7 1 SECTION VII VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESS CIRCUIT ...
Page 77: ...8 1 SECTION VIII CCD CAMERA CIRCUIT ...
Page 80: ...9 1 SECTION IX FLUORESCENT LAMP INVERTER CIRCUIT ...
Page 83: ...9 4 3 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM Fig 9 5 Cicuit diagram ...
















































