13
/
16
13
electrical outlet.
Tungsten Inert Gas
(
TIG
)
Welding
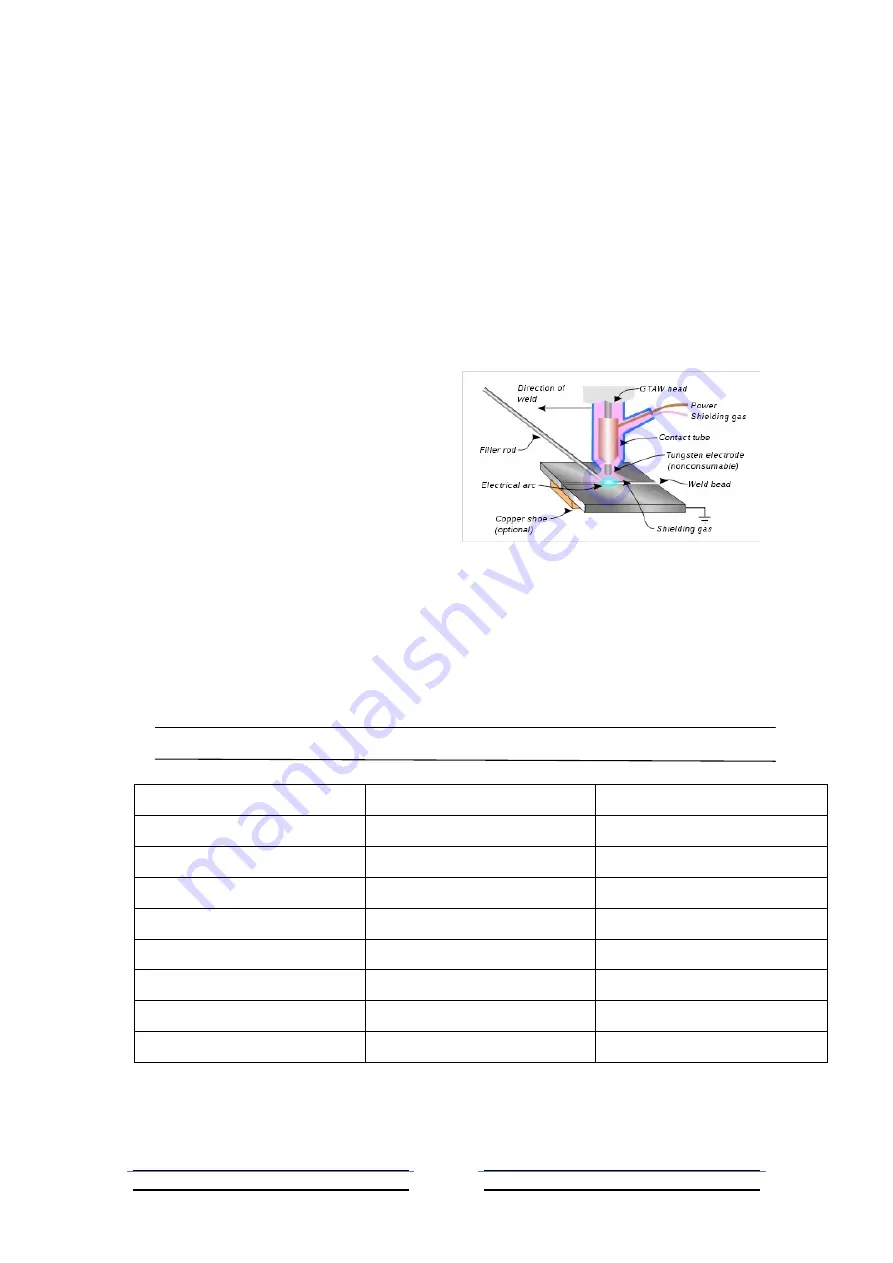
Gas tungsten arc welding
(
GTAW
),
also known as
tungsten inert gas
(
TIG
)
welding
, is an arc welding process that
uses a no consumable tungsten electrode
to produce the weld. The weld area is
protected from atmospheric contamination
by a shielding gas (usually an inert gas
such as argon), and a filler metal is
normally used, though some welds, known
as autogenously welds, do not require it. A
constant-current welding power supply
produces energy which is conducted
across the arc through a column of highly
ionized gas and metal vapors known as
plasma. TAW is most commonly used to
weld thin sections of stainless steel and
non-ferrous metals such as aluminum,
magnesium, and copper alloys. The
process grants the operator greater
control over the weld than competing
procedures such as shielded metal arc
welding and gas metal arc welding,
allowing for stronger, higher quality welds.
However, GTAW is comparatively more
complex and difficult to master, and
furthermore, it is significantly slower than
most other welding techniques. A related
process, plasma arc welding, uses a
slightly different welding torch to create a
more focused welding arc and as a result
is often automated.
TIPS FOR TIG WELDING
Welding current(A)
Tungsten diameter(mm)
Argon flux(L/min)
5
~
15
0.5
3
~
7
10
~
65
1.0
4
~
8
55
~
120
1.6
6
~
9
85
~
150
2.0
6
~
10
120
~
200
2.4
7
~
10
200
~
320
3.2
10
~
15
320
~
400
4.0
12
~
20
400
~
640
4.8
15
~
25
Summary of Contents for 597076
Page 1: ...1 16 1 ...


































