March 2021
Service and Repair Manual
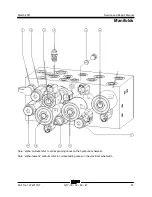
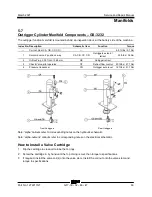
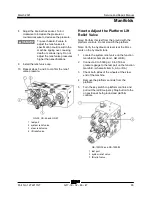
Manifolds
Part No. 1272217GT
GS
™
-30 • 32 • 46 • 47
71
How to Test a Coil Diode
Genie incorporates spike suppressing diodes in all
of its coils. Properly functioning coil diodes protect
the electrical circuit by suppressing voltage spikes.
Voltage spikes naturally occur within a function
circuit following the interruption of electrical current
to a coil. Faulty diodes can fail to protect the
electrical system, resulting in a tripped circuit
breaker or component damage.
Electrocution/burn hazard.
Contact with electrically charged
circuits could result in death or
serious injury. Remove all rings,
watches and other jewelry.
1 Test the coil resistance. Refer to Repair
Procedure,
How to Test a Coil
.
2 Connect a 10
Ω
resistor to the negative
terminal of a known good 9V DC battery.
Connect the other end of the resistor to a
terminal on the coil.
Note: The battery should read 9V DC or more
when measured across the terminals.
Resistor, 10
Ω
Genie part number
27287
3 Set a multimeter to read DC amperage.
Note: The multimeter, when set to read DC
amperage, should be capable of reading up to
800 mA.
4 Connect the negative lead to the other
terminal on the coil.
Note: If testing a single terminal coil, connect the
negative lead to the internal metallic ring at either
end of the coil.
1 multimeter
2 9V DC battery
3 10
Ω
resistor
4 coil
Note: Dotted lines in illustration indicate a reversed
connection as specified in step 6.
5 Momentarily connect the positive lead from
the multimeter to the positive terminal on the
9V battery. Note and record the reading.
6 At the battery or coil terminals, reverse the
connections. Note and record the current
reading.
Result: Both current readings are greater than
0 mA and are different by a minimum of 20%.
The coil is good.
Result: if one or both current readings are
greater than 0 mA, or if the two current
readings do not differ by a minimum of 20%,
the coil and/or its internal diode are faulty and
the coil should be replaced.