82
PBX Networking
Connections
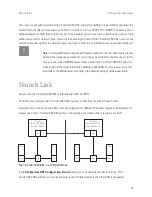
Example of a PBX network
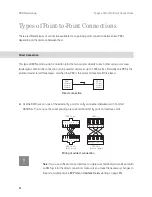
Various line types and transmission protocols can be used for point-to-point connections. The required
network topology (distance, connection capacity) determines which type of point-to-point connection is most
suitable.
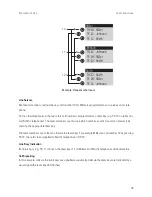
Protocol: Q.SIG or DSS1
The Q.SIG protocol, designed for ISDN point-to-point connections, is the preferable choice as the trans-
mission protocol; alternatively, the DSS1 protocol, designed for ISDN dial-up connections in the Euro-ISDN,
can be used. Certain PBX networking features can only be used with the Q.SIG protocol, however. In par-
ticular, the identifier indicating whether a call is internal or external cannot be transmitted using DSS1.
Both protocols implement communication on several protocol layers:
■
L1: Layer 1 defines the physical line properties and the electrical coding of signals.
■
L2: Layer 2 enables communication via individual error-protected channels that are independent of each
other.
■
L3: Layer 3 defines the administration of the individual channels and implements the features designed
for ISDN.
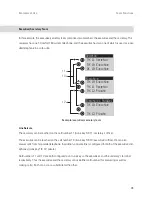
Master/Slave
For an ISDN connection, it is possible to determine which PBX is the protocol master and which the protocol
slave. This relationship can be determined for all three protocol layers independently of one another.
Point-to-point
connection
Trunk line
PBX
PBX
PBX
PBX
PBX
Summary of Contents for 930 DSL
Page 1: ...T Comfort 930 DSL Mounting and Commissioning...
Page 2: ......
Page 10: ...8...
Page 148: ...146 Index Notes...
Page 149: ...147 Index Notes...
Page 150: ...148 Index Notes...
Page 151: ......
Page 152: ...As of 01 09 2006 Deutsche Telekom AG T Com Bereich Endger te Postfach 20 00 53105 Bonn...