Chapter 3: Wiring
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98)
21
© Saftronics, Inc.
3.3
Wiring the Control Circuit
The following table outlines the functions of the control circuit terminals. Wire according to each terminal function.
3.3.1
Functions of Control Circuit Terminals
Table 8
Control Circuit Terminals
Classi-
fication
Terminal
Signal Function
Description
Signal Level
S1
Forward run/stop
Forward run when closed, stop when open
S2
Reverse run/stop
Reverse run when closed,
stop when open
S3
External fault input
Fault when closed,
normal state when open
S4
Fault reset input
Reset when closed
S5
Multi-step speed reference 1
Effective when closed
S6
Multi-step speed reference 2
Effective when closed
Multi-function contact
inputs (n035 to n039)
Sequence Input Signal
SC
Sequence control input
common terminal
Photo-coupler insulation
Input:
+
24 VDC 8 mA
FS
+
15 V
Power supply output
For analog command
+
15 V power supply
+
15 V
(Allowable current 20 mA
maximum)
FV
Frequency reference input
(voltage)
0 to
+
10 V/100%
0 to
+
10 V (20 k
Ω
)
FI
Frequency reference input
(current)
4 to 20 mA/100%
n042 = 0 : FV
effective
n042 = 1 : FI
effective
4 to 20mA (250
Ω
)
FC
Common terminal for control
circuit
0 V
Analog Input Signal
G
Connection to shield sheath
of signal lead
M1
M2
During running (NO contact)
Closed when running
Multi-function
contact output
(n041)
Dry contact
Contact capacity:
250 VAC 1 A or less
30 VDC 1 A or less
MA
MB
Sequence Output Signal
MC
Fault contact output (NO/NC
contact)
Fault when closed between
Terminals MA and MC.
Fault when open between
Terminals MB and MC.
Multi-function
contact output
(n040)
Dry contact
Contact capacity:
250 VAC 1 A or less
30 VDC 1 A or less
AM
Frequency meter output
Analog Output
Signal
AC
Common
0 to
+
10 V/100% frequency
Multi-function
analog monitor 1
(n048)
0 to
+
10 V 2 mA or less
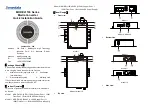
G
S1
S2
S3
SC
SC
S4
S5
S6
FV
FI
FS
FC
AM
AC
M1
M2
MA
MB
MC
Figure 11 Control Circuit Terminal Arrangement
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor