2916050
30
GB
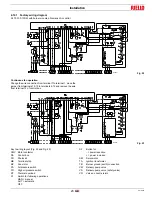
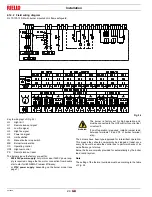
Start-up, calibration and operation of the burner
5.6
Burner operation
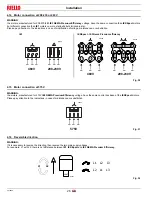
5.6.1
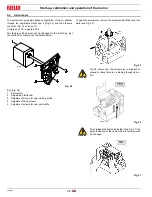
Burner starting
•
Operating control closes, the motor starts.
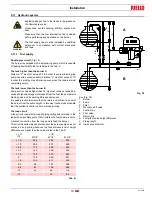
The pump 3)(Fig. 40) draws the fuel from the tank through the
piping 1) and pumps it under pressure for delivery.
The piston 4) rises and the fuel returns to the tank through the
piping 5) - 7).
The screw 6) closes the by-pass heading towards suction and
the de-energized solenoid valves 8) - 9) - 2) close the passage
to the nozzle.
•
Servomotor starts: 130° rotation to right, until contact is made
on cam 1. The air damper is positioned on MAX. output.
•
Pre-purge stage with air delivery at MAX. output.
•
Servomotor rotates to left until contact is made on cam 3.
•
Air damper and pressure regulator are positioned on MIN out-
put.
•
Ignition electrode strikes a spark.
•
Solenoid valves 8) - 9) - 2) open; the fuel passes through the
piping 10) and filter 11), and enters the nozzle.
A part of the fuel is then sprayed out through the nozzle, ignit-
ing when it comes into contact with the spark: flame at a low
output level; the rest of the fuel passes through piping 12 at the
pressure adjusted by the regulator 13, then, through piping 7),
it goes back into the tank.
•
The spark goes out.
•
The starting cycle ends.
5.6.2
Steady state operation
At the end of the starting cycle, the servo-motor control then pass-
es to load control for boiler pressure or temperature.
If the temperature or pressure is low (and the load control is conse-
quently closed), the burner progressively increases output up to
MAX.
If subsequently the temperature or pressure increases until the
load control opens, the burner progressively decreases output
down to MIN.
The burner shuts off when demand for heat is less than the heat
supplied by the burner in the MIN output.
The servomotor returns to the 0° angle limited by contact with cam
2. The air damper closes completely to reduce thermal dispersion
to a minimum.
Every time output is changed, the servomotor automatically modi-
fies oil delivery (pressure regulator) and air delivery (fan damper).
5.6.3
Firing failure
If the burner does not fire, it goes into lock-out within 5 s of the
opening of the light oil valve.
5.6.4
Firing failure
If the flame should go out for accidental reasons during operation,
the burner will lock out in 1 s.
D2444
Fig. 40