CHAPTER 3 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
User’s Manual S14054EJ4V0UM
42
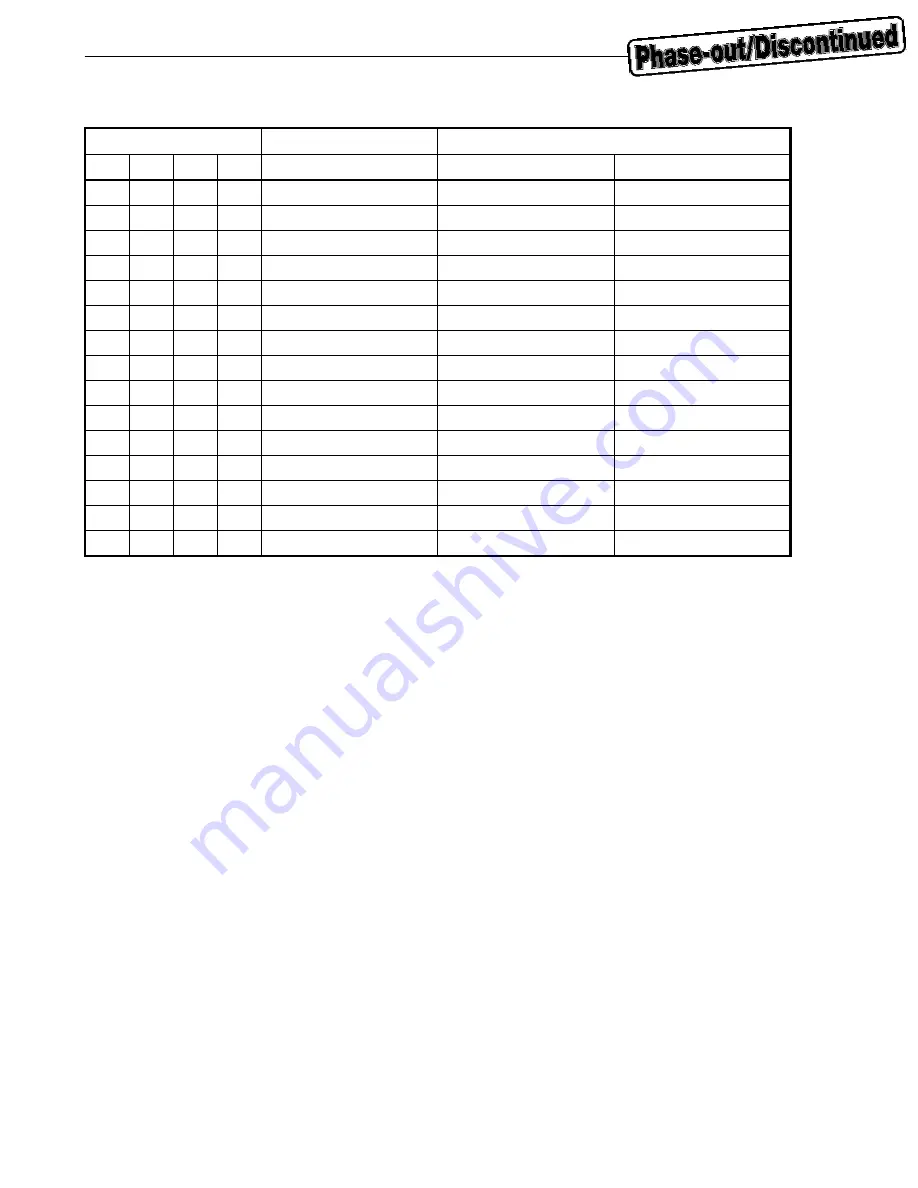
Table 3-4. FDQ Pin and Receive Data Attribute (64-Bit Single Bus)
FDQ Pin
Data Attribute
Valid Data Byte Position
[3]
[2]
[1]
[0]
Little Endian
Big Endian
0
0
0
0
Idle
–
–
0
0
0
1
Data start
FD[63:0]
FD[63:0]
0
0
1
0
Intermediate data
FD[63:0]
FD[63:0]
0
0
1
1
Reserved
FD[63:0]
FD[63:0]
0
1
0
0
Status information (first)
FD[31:0]
FD[63:32]
0
1
0
1
Status information (last)
FD[31:0]
FD[63:32]
0
1
1
×
Reserved
–
–
1
0
0
0
Data end 0
FD[63:0]
FD[63:0]
1
0
0
1
Data end 1
FD[7:0]
FD[63:56]
1
0
1
0
Data end 2
FD[15:0]
FD[63:48]
1
0
1
1
Data end 3
FD[23:0]
FD[63:40]
1
1
0
0
Data end 4
FD[31:0]
FD[63:32]
1
1
0
1
Data end 5
FD[39:0]
FD[63:24]
1
1
1
0
Data end 6
FD[47:0]
FD[63:16]
1
1
1
1
Data end 7
FD[55:0]
FD[63:8]
For details of how to append status information, refer to
3.7.1 (2) (c) Appending status information
. For
details of little endian/big endian, refer to
3.7.1 (4) Little endian/big endian
.
When reading of the one packet specified by RXFPT has been completed, the
µ
PD98431 then makes the
RXFA signal high if any of the ports is ready for reading receive data, outputs the port number to RXFPT,
and waits for reading the next receive data.
The RXFA signal remains high if receive data ready to be read exists in the port indicated by RXFPT.
However, the RXFA signal goes low once if control is transferred to another port by the SKIP signal while the
first port is read.
The sequence in which the ports of the
µ
PD98431 transfer receive data is predetermined. Port 0 first
transfers data, followed by port 1, port 2, and so on. After port 7 has transferred data, port 0 transfers data
again. If one packet of receive data has not been completely accumulated in the next port when it is
selected, however, that port is skipped, and the port after the next one is selected.
Figure 3-8 shows an example of timing at which reading the next port is started after reading of the receive
port from a specific port has been completed.






























