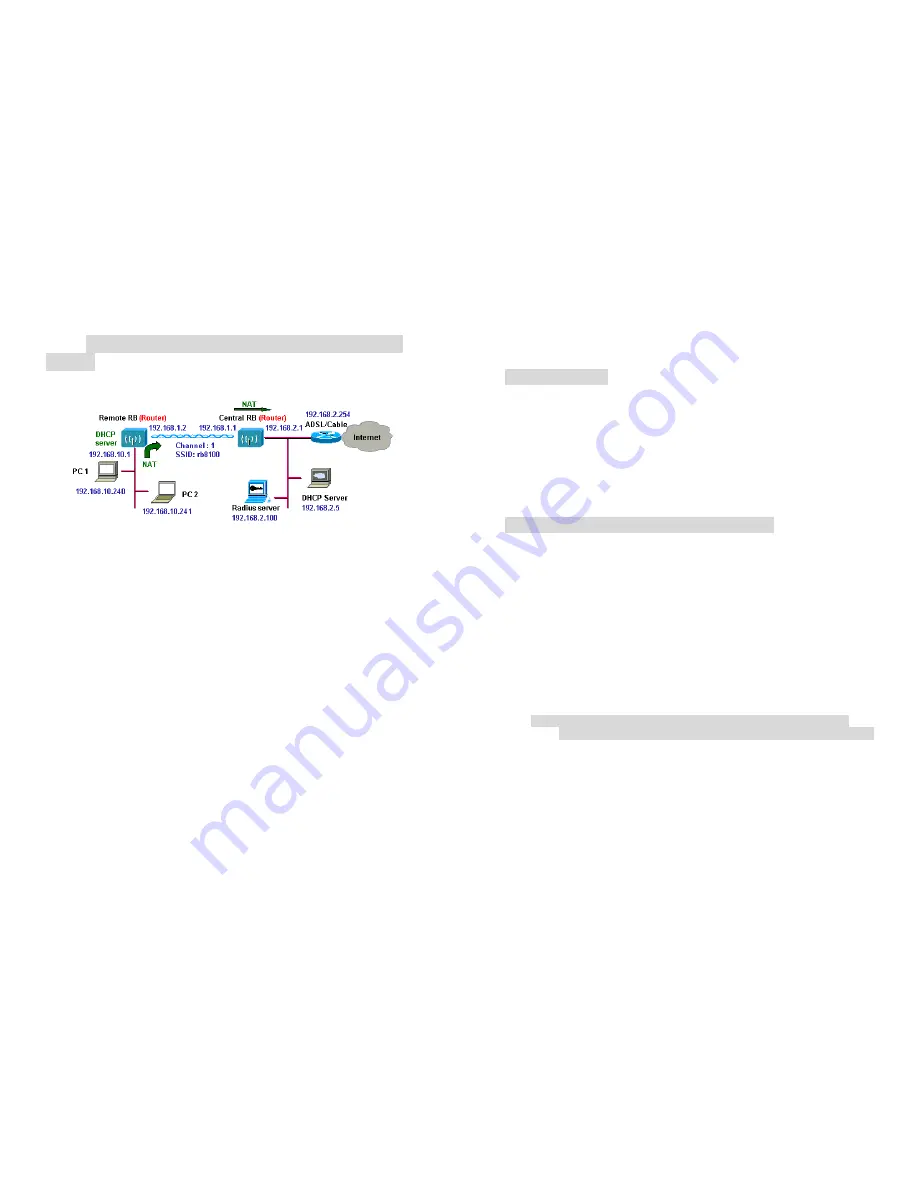
2.4
Remote Wireless Router-to-Central Wireless
Router
1. Set the Central RB run as a Wireless Router (
Wireless Interface IP is
192.168.1.1, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.2.1, default route is
192.168.2.254
).
2. Set Wireless parameters on Central RB: Channel (
1
) and SSID
(
wireless
).
3. Set the Remote RB as a Wireless Router (
Wireless Interface IP is
192.168.1.2, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.10.1, default route is
192.168.1.1
)
.
4. Set Wireless parameters on Remote RB: Channel (
1
) and SSID
(
wireless
), these parameters must same with Central RB.
5. Set the DHCP server service on the Remote RB and apply it on
Ethernet Interface.
6. The Remote RB assigns IP address to PC1 and PC2.
The operator can also turn off NAT behavior on Central RB and turn
on NAT behavior on Remote RB. In this case, any outgoing packets
will transfer to 192.168.1.2
Remote RB:
turn on NAT on Wireless Interface.
The operator can also turn on NAT behavior on Central RB and turn
on NAT behavior on Remote RB.
Central RB: turn on NAT on Ethernet interface.
Remote RB:
turn on NAT on Wireless Interface.
Chapter 3. Web Access
Web Connection
The Outdoor Wireless Access Router/Bridge (RB) supports access to the
configuration system through the use of an HTTP Interface (web browser).
Before configuring the RB, you need to know the IP Address assigned to
the unit.
When shipped from the factory, the IP Address (192.168.2.1) was assigned
to the RB by default.
To start a web connection use:
http://192.168.2.1/
Identify the IP Address assigned to the unit
However, the IP Address may be changed and you cannot connect the unit
using the default IP Address. In this case, you must identify the RB IP
Address before configuration. To identify the IP Address, you can use the
Serial Port to gain access the current network status. To start a Serial Port
connection:
1.
Attach a serial data (RS-232) cable to the Serial Port Adapter.
Connect the other cable end to a terminal or a PC running a terminal
emulation program. Use a 9-pin female to 9-pin female NULL Modem
cable.
2.
Set the terminal to
115200
Baud,
No
-Parity,
8
data bits,
1
Stop bit,
and ANSI compatible.
Note: Running a terminal emulation program on your PC, such as
HyperTerminal, and then set the following connection properties:
Click the
Start icon
>
Program
>
Accessories
>
Communication
>
Terminal
.
Create a new connection file, and then select a Com Port
<
COM1, COM2, etc., depending on your PC>
with
115200
bps /
8-bits / 1-stop
.
Click the properties icon in the
Tool Bar > setting > select
Emulation terminal
VT100
>
ok
.






















