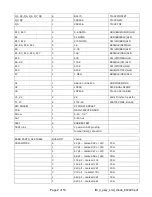
Page 11 of 16 ft8_II_assy_smd_diode_072020.pdf
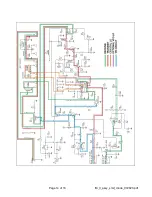
Theory of operation:
The Digital DSB transceiver is built around the ubiquitous SA602/612A mixer-oscillator chip. It
provides both the receive and transmit functions.
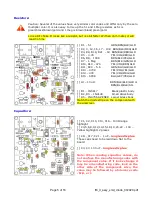
Receiver:
The antenna is first routed through the transmitter's Low Pass Filter (LPF) and then into a BS170
MOSFET, which is the receiver input T/R switch. The received signal is coupled into a new High
Pass Filter (HPF) circuit comprised of C26 and L1. Stray capacitance (~88pF) resonates L1 to
about the operating frequency.
The received input signal is applied to the input of the SA602 mixer (U1) to produce the base line
audio output. The Local Oscillator is either the crystal on the band module using the internal
oscillator of the SA602, or an optional Digital VFO.
U2b, one half of a LM358 op amp, provides audio gain for decent sensitivity. A non-inverting
configuration is used so that the input can be high impedance, allowing for reasonably small value
input coupling caps. The gain is set to 47. The amplifier then drives an audio level pot so the
audio level can be adjusted to a level suitable for your PC sound card. Q1 provides muting of the
audio output by shorting the input to the audio level pot to ground.
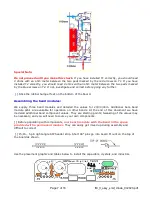
Transmitter:
The SA602/612 requires very little input signal to saturate. Therefore a resistor divider is placed
between the audio input from the sound card to the mixer input. This allows you to set the audio
output from the sound card to a reasonable level and not overdrive the mixer.
The other half of the LM358 (U2a) is used as a VOX circuit. The peak detector circuit of D3 and
C12 isn't required for FT8 operation, but is included if one wishes to experiment with other modes
where the audio input can drop to zero for short periods of time.
The output of the Peak Detector activates the T/R switching.
Q4 turns on, activating this sequence:
Q2 is turned off, which disconnects the antenna from the mixer input.
Q5 is turned on, which switches on the power to the transmit circuits.
Q1 is turned on, muting the audio output.
Q3 is turned on, shunting any transmit RF which might leak through Q1.
Q6-Q7-Q8 amplifies the RF output from the mixer to a level sufficient to drive the PA. The PA is
comprised of three BS170 MOSFETS in parallel. Bias is applied to the gates to place the amplifier
into linear mode. This also reduces the amount of drive needed since the input signal does not
have to first exceed the ~2.5V it takes to start to turn on the MOSFETS. The signal then goes to
the Low Pass Filter (LPF) and finally the antenna.
Power to the circuits is supplied by a 9V, 1A regulator. This ensures the power output remains in a
safe operating area and if there is a problem, the internal over current protection will shut down
the regulator. Since the maximum operating voltage of the SA602/612 is 9V, a diode is placed in
series with the 9V supply insure the voltage to the chip does not exceed the maximum
recommended supply voltage.