I/O interface description
GVI Product Manual: Frames C, D & E
36
192-300300N1 GVI Frames C, D & E 2019-9
8.9
High Side IN and Out
8.9.1. Function
CAUTION
High current – risk of damage to equipment
Keep Cable length from B+ to HIGH_SIDE_IN as short as possible. High current on Open drain
outputs with PWM can cause ripple voltage on the High side in and out.
Ripple current must be less than 2 A continuous.
In addition to the Open drain outputs there is also a high side switch for critical safety functions, providing
redundancy to turn OFF the Open Drain loads. If an Open drain output is short circuited, it is possible to turn
OFF the High side switch to disconnect load. In inverters with dual CPU:s, the high side switch can be
disabled from both main and supervision CPU independently.
The High side switch has a maximum output current. The high side switch has only ON/OFF control.
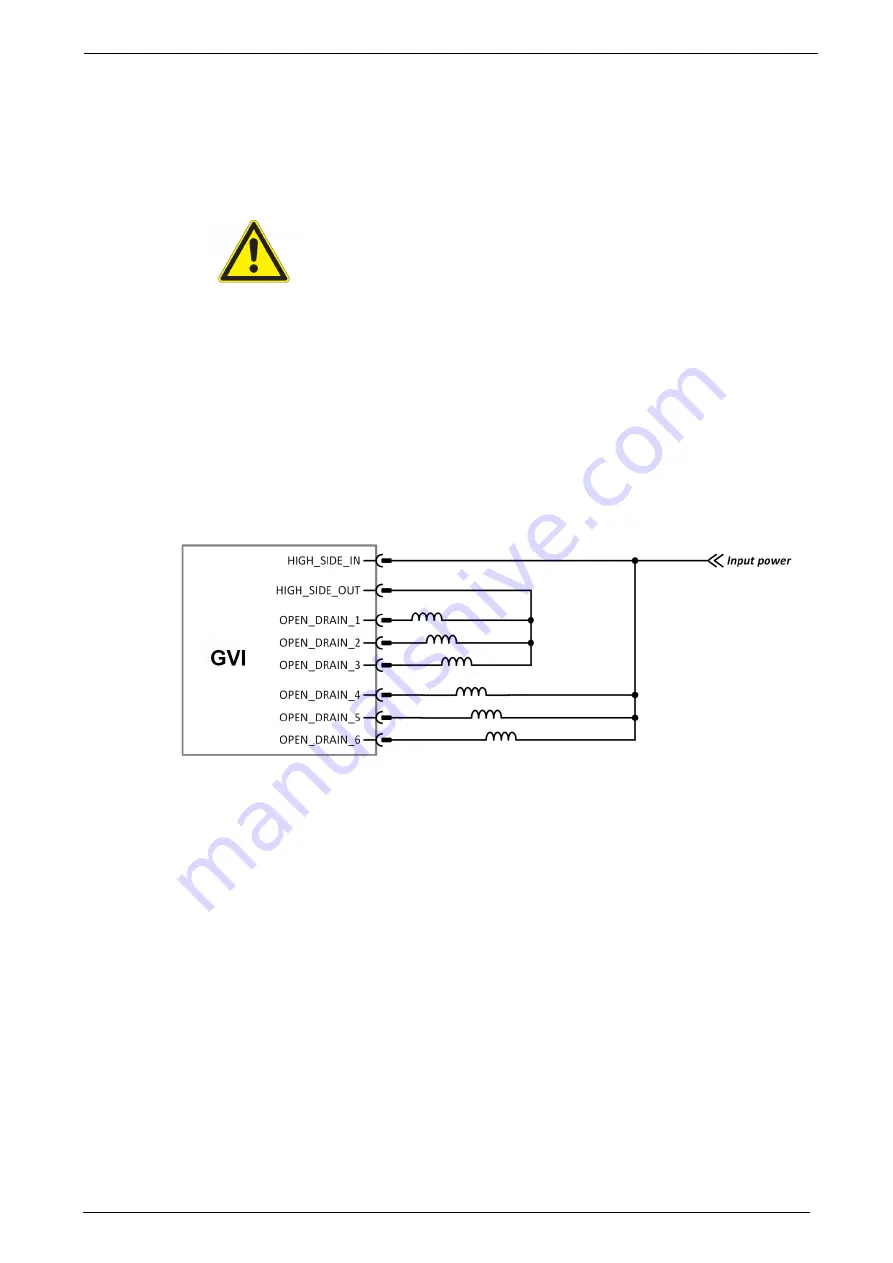
Voltage to power the loads driven should be applied to the HIGH_SIDE_IN pin, and the load should be
connected between HIGH_SIDE_OUT and an open drain output as shown in Figure 22.
Figure 22 Example use of HIGH_SIDE_IN/OUT to ensure path to internal free-wheeling diodes
High Side In voltage has a minimum required value for correct function (see chapter 13.4.6). A voltage below
this value will shut down the High side output and indicate short circuit detection (needs to be handled in the
application). The High Side Out voltage is monitored and the high side in is monitored by a digital input.
The GVI has an internal pre-charge PTC-resistor with a series diode connected between HIGH_SIDE_IN
and the capacitor bank. The inrush current limiting resistance can be activated and deactivated in the motor
controller software.
8.9.2. Protection
Internal hardware short circuit detection and a capacitor to B- on input and output are provided for ESD
protection.
For fuse F3, shown in Figure 10, see chapter 7.9.
















































