65
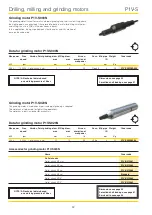
Stainless Steel Air Motors
P1V-S
40
20
7 bar
6 bar
5 bar
4 bar
3 bar
60
80
100
160
120
140
200
220
240
180
100
100
120
20
40
60
80
20
40
60
80
M
M [%]
n [%]
Q
P
Q [%], P [%]
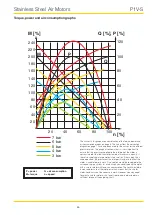
Torque, power and air consumption graphs
P = power
Q = air consumption
M = torque
n = speed
The curves in this graph are a combination of the torque, power and
air consumption graphs on page 6. The values from the correction
diagram on page 7 have also been used for the curves for the different
pressure values. The graph also shows that is it very important to
ensure that the pressure supplied to the inlet port of the motor is
correct, in order to allow the motor to work at maximum capacity. If
the valve supplying a large motor is too small, or if the supply line is
underspecified, the pressure at the inlet port may be so low that the
motor is unable to do its work. One solution would be to upgrade the
valve and supply system, or alternatively you could replace the motor
with a smaller motor with lower air consumption. The result would be
increased pressure at the inlet port, which means that the smaller
motor could carry out the necessary work. However, you may need
to select a smaller motor with a lower free speed in order to obtain
sufficient torque at the outgoing shaft.
Summary of Contents for 1P1V-S020A00005
Page 66: ...66 Stainless Steel Air Motors P1V S...
Page 67: ......