5. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
5-14
April
2002
8000-A2-GB26-70
Client Cannot Reach Service Node
If the problem persists after the above items are checked, the client-to-service
node segment of the network is functional.
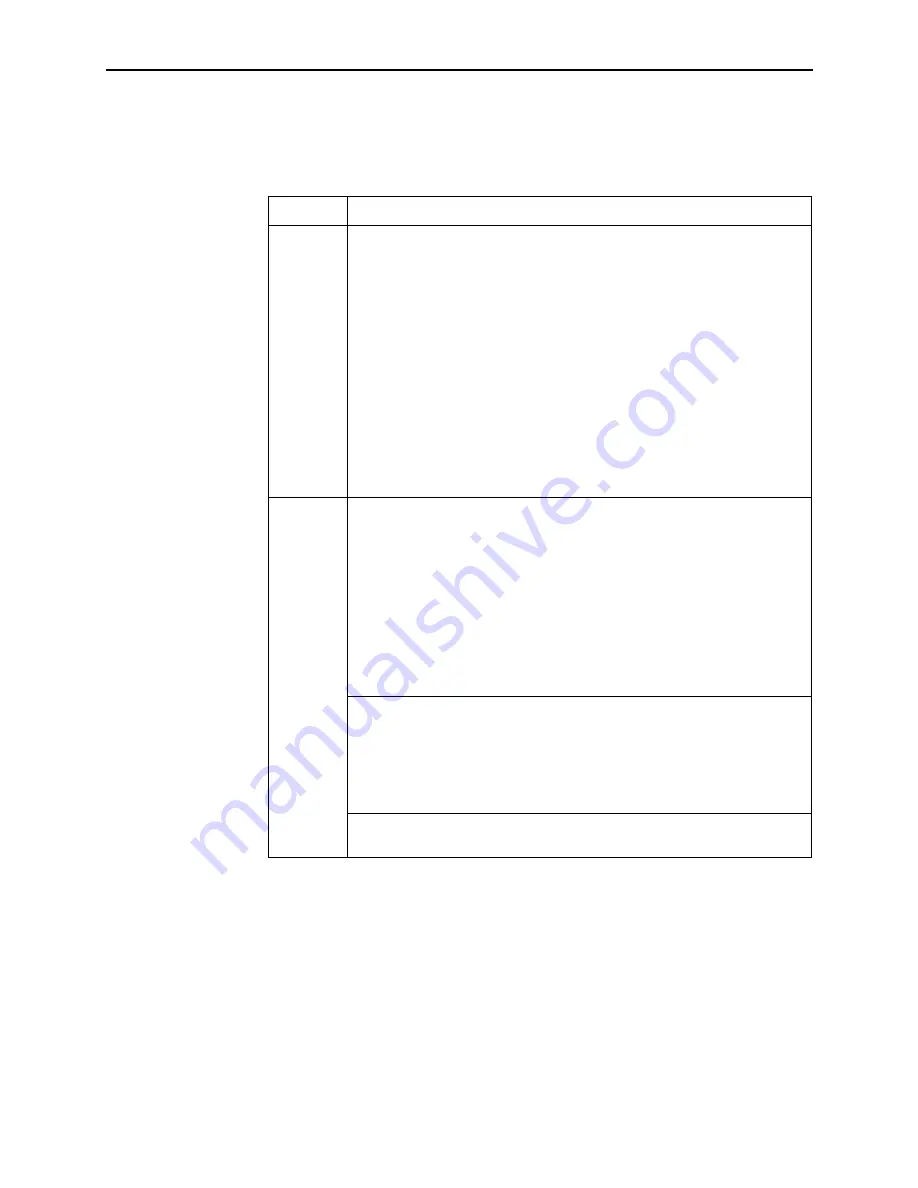
Table 5-4.
Client-to-Service Node Segment
Layer
Solution
Layer 1 –
Physical
1. Make sure the PWR LED on the front of the Service Node is lit. Use only
the power adapter shipped with the unit.
2. To verify connection to the client, make sure the ETHERNET LED on the
front of the Service Node is lit.
3. Make sure there is a physical connection between the Service Node and
the Network Interface Card (NIC). If there is a LINK LED on the NIC card,
make sure it is lit.
4. If there is a hub, check its cables and LEDs.
5. Make sure the correct type of cable is being used between the client and
the Service Node. A crossover cable should be used if the client is not
connected to a LAN hub.
6. Make sure the NIC and drivers are correctly installed.
7. Make sure the correct Service Node firmware is being used.
Layer 2 –
Network
1. If static addressing is used, make sure the client has its correct IP
address and subnet mask by entering the following:
– Windows 95: winipcfg
– Windows NT: ipconfig/all
For other operating systems, use help or see the appropriate manual.
2. Restart the client after a static IP address has been added or changed.
3. Make sure the client can ping its own IP address. This confirms the IP
address was successfully accepted by the computer.
4. Check the PC’s default gateway to make sure it is functioning properly.
1. If dynamic addressing is being used and the client cannot get an IP
address from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server,
statically configure an IP address and then verify that the client can ping
the DHCP server.
2. After the client reaches the server, remove the IP address and return the
system to dynamic (DHCP) addressing.
Make sure there are 32 or fewer DHCP users active on the port at any given
time. Only 32 users are entered into the host table.






























