Issue 2.0
SV9100 Networking Manual
5-15
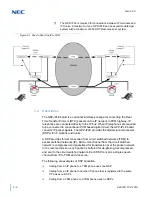
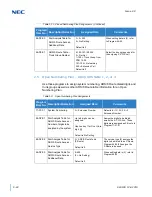
VOIP packet with RTP header compression
Voice Activity Detection
(VAD) is suppression of silence packets from
being sent across the network. In a VoIP network all conversations are
packetized and sent, including silence. On an average a typical
conversation contain anywhere from 35% ~ 45% silence. This can be
interrupted as 35% ~ 45% transmission of VoIP packets, having no audio,
use valuable bandwidth. With the VAD option enabled, the transmitting of
packets stops after a threshold is met determining silence. The receiving
side then injects comfort noise into the call so it does not appear the call has
dropped.
1.5.4
Bandwidth Calculations
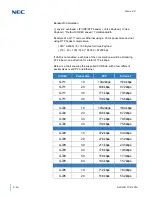
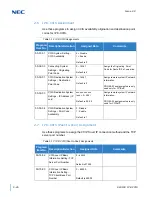
The first step in calculating the bandwidth of a call is determining how many
bytes the voice payload is going to use. The amount is directly affected by
the CODEC and packet size. Below are the supported default CODEC
speeds for CCISoIP.
G.711 = 64000 bps
G.722 = 64000 bps
G.729 = 8000 bps
G.726 = 32000 bps
G.723 = 5400 bps
1.5.5
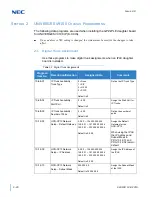
Payload Calculation Voice
(Packet size * Codec bandwidth) / 8 = Voice Payload in Bytes
Example of G.711 with a 20 ms packet size
(.020 * 64000) /8 = 160 Bytes
Example of G.729 with a 30 ms packet size
(.030 * 8000) /8 = 30 Bytes
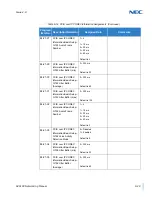
Now that you have the voice payload in bytes you can now calculate the
overall bandwidth including the layer 2 media. Below are some of the
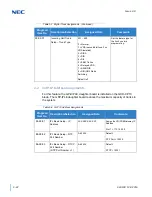
common layer 2 media types and their overhead.
Ethernet = 18 Bytes
802.1Q/P Ethernet = up to 32 bytes
PPP = 9 Bytes
Frame Relay = 6 Bytes
Multilink Protocol = 6 Bytes
Compressed
Header 2 ~ 4-bytes
Voice-Payload
Summary of Contents for Univerge SV9100
Page 1: ...Networking Manual A50 035910 004 AU Issue 2 0...
Page 20: ...xviii Table of Contents Issue 2 0...
Page 26: ...xxiv List of Figures Issue 2 0...
Page 33: ...Book 1 SV9100 K CCIS...
Page 49: ...Issue 2 0 1 16 General Information US Only Figure 1 15 Circuit Identification Codes CIC...
Page 53: ...Issue 2 0 1 20 General Information US Only...
Page 61: ...Issue 2 0 2 8 Hardware Installation US Only...
Page 195: ...Issue 2 0 4 116 Features and Specifications...
Page 242: ...Book 2 SV9100 IP Networking...
Page 256: ...Issue 2 0 2 12 IP Networking...
Page 312: ...Issue 2 0 4 48 Programming...
Page 376: ...Issue 2 0 6 30 SIP Trunking...
Page 391: ...Issue 2 0 7 14 H 323 Trunking...
Page 467: ...Issue 2 0 8 76 IP Multiline Station SIP...
Page 551: ...Issue 2 0 10 64 SV9100 NetLink Conditions None Feature Cross Reference None...
Page 567: ...Issue 2 0 10 80 SV9100 NetLink Conditions None Feature Cross Reference None...
Page 579: ...Issue 2 0 11 6 NAPT...
Page 580: ...Issue 2 0 SV9100 Networking Manual 11 7...
Page 581: ...Issue 2 0 11 8 NAPT...
Page 582: ...Issue 2 0 SV9100 Networking Manual 11 9...
Page 583: ...Issue 2 0 11 10 NAPT...
Page 584: ...Issue 2 0 SV9100 Networking Manual 11 11...
Page 595: ...Issue 2 0 12 4 All DSP Busy Indication...
Page 671: ...Issue 2 0 13 76 AspireNet Conditions None Feature Cross Reference None...
Page 685: ...Issue 2 0 13 90 AspireNet Department Calling Flexible System Numbering Intercom...
Page 707: ...Issue 2 0 13 112 AspireNet Default Trunk Port Number Name 1 Line 001 2 Line 002 400 Line 400...
Page 713: ...Issue 2 0 13 118 AspireNet Department Calling...
Page 765: ...Issue 2 0 13 170 AspireNet...