5 - 44 WiNG 5.7.1 Access Point System Reference Guide
10. Select
OK
to save the changes made to the port channel Basic Configuration. Select
Reset
to revert to the last saved
configuration.
11. Select the
Security
tab.
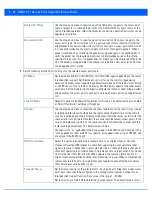
Figure 5-29
Port Channels - Security tab
12. Refer to the
Access Control
section. As part of the port channel’s security configuration, Inbound IPv4 IP, IPv6 IP and MAC
address firewall rules are required.
Use the
IPv4 Inbound Firewall Rules, IPv6 Inbound Firewall Rules
and
Inbound MAC Firewall Rules
drop-down
menus to select the firewall rules to apply to this profile’s port channel configuration. The firewall inspects IP and MAC
traffic flows and detects attacks typically not visible to traditional wired firewall appliances
Use the
IPv4 Inbound Firewall Rules
drop-down menu to select the IPv4 specific firewall rules to apply to this profile’s
port channel configuration. IPv4 is a connectionless protocol for packet switched networking. IPv4 operates as a best effort
delivery method, as it does not guarantee delivery, and does not ensure proper sequencing or duplicate delivery (unlike
(TCP). IPv4 hosts can use link local addressing to provide local connectivity.
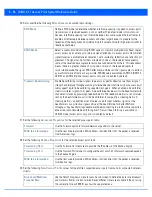
Tag the Native VLAN
Select this option to tag the native VLAN. Access points support the IEEE 802.1Q specification
for tagging frames and coordinating VLANs between devices. IEEE 802.1Q adds four bytes to
each frame identifying the VLAN ID for upstream devices that the frame belongs. If the
upstream Ethernet device does not support IEEE 802.1Q tagging, it does not interpret the
tagged frames. When VLAN tagging is required between devices, both devices must support
tagging and be configured to accept tagged VLANs. When a frame is tagged, the 12 bit frame
VLAN ID is added to the 802.1Q header so upstream Ethernet devices know which VLAN ID the
frame belongs to. The device reads the 12 bit VLAN ID and forwards the frame to the
appropriate VLAN. When a frame is received with no 802.1Q header, the upstream device
classifies the frame using the default or native VLAN assigned to the Trunk port. The native
VLAN allows an Ethernet device to associate untagged frames to a VLAN when no 802.1Q
frame is included in the frame. This setting is disabled by default.
Allowed VLANs
Selecting
Trunk
as the mode enables the Allowed VLANs parameter. Add VLANs that
exclusively send packets over the port channel.
Summary of Contents for WiNG 5.7.1
Page 1: ...WiNG 5 7 1 ACCESS POINT SYSTEM REFERENCE GUIDE ...
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...WING 5 7 1 ACCESS POINT SYSTEM REFERENCE GUIDE MN001977A01 Revision A April 2015 ...
Page 4: ...ii WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 24: ...1 4 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 36: ...2 12 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 72: ...3 36 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 470: ...5 386 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 472: ...6 2 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide Figure 6 1 Configuration Wireless menu ...
Page 624: ...7 46 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 724: ...9 56 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 783: ...12 35 Figure 12 46 Device Summary screen 4 Click File Management ...
Page 816: ...12 68 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1006: ...13 190 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1026: ...14 20 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1028: ...A 2 WiNG 5 7 1 Access Point System Reference Guide ...
Page 1089: ......
Page 1090: ...MN001977A01 Revision A April 2015 ...