EA-1 User Manual
14
Click on Set IP Address and follow the instructions above to fix the IP address to a good value.
Using the “Setup Device” screen:
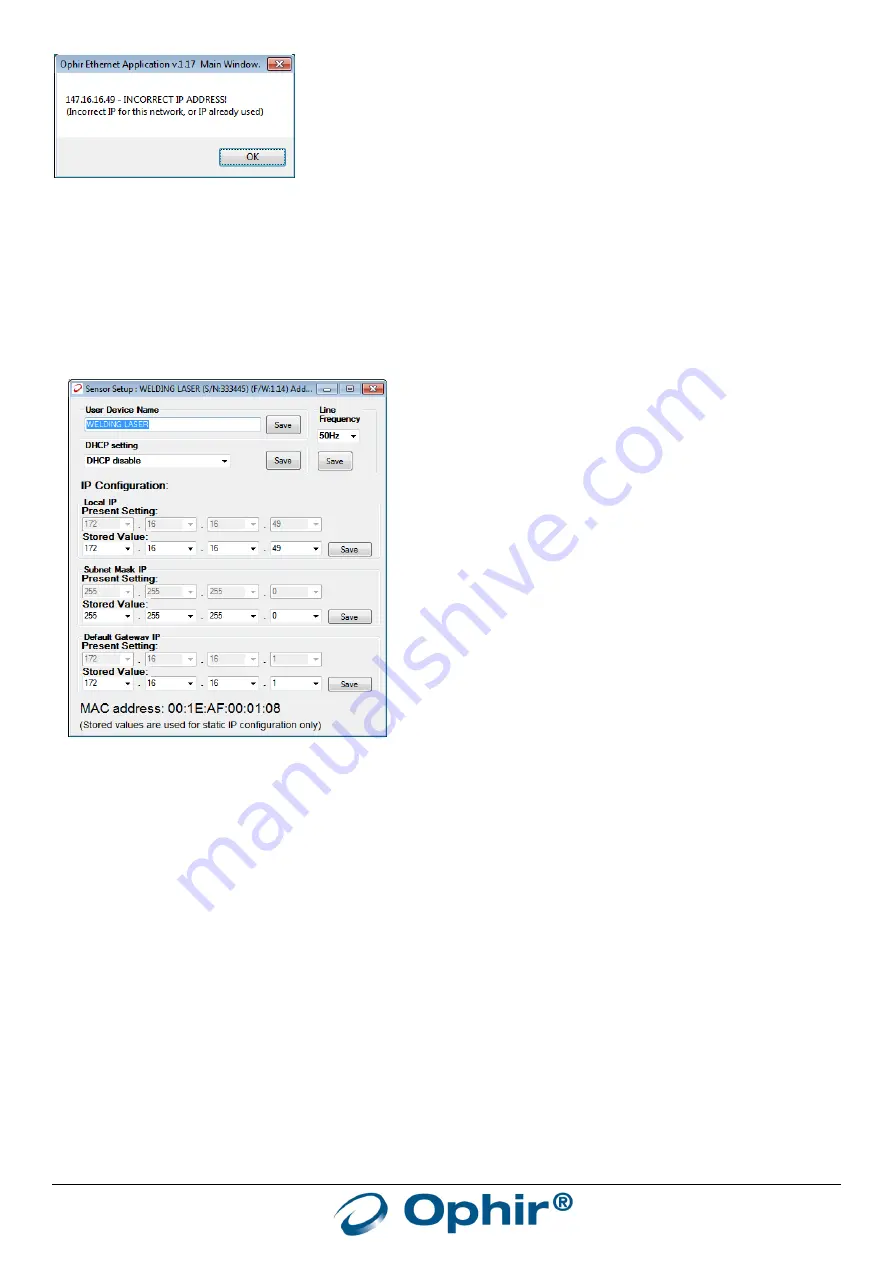
An alternative method to change the IP settings is to use the “Select-Device” screen. After selecting the sensor in the
main window (by clicking on it in the “Sensor Choice” window as shown above), enter the “Setup-Device” screen.
Choose the new settings by hand and press “Save”. Note that this option is available only if the present IP address is
acceptable for the network.
Note:
If the user changes the IP address to a new setting and presses “Save”, the new value will be saved to local
memory inside the device and will be used the next time the device powers up.
However, if the user then tries to restore the value back to its original setting and then presses “Save” again before
exiting the application and resetting the device, a message “Unchanged” will be given, and the value will not be
changed inside the device. The next time the device is powered up, it will use the new setting and not the original
setting. This behavior is the same whether connected via Ethernet or USB.
This software application also provides a search feature which allows the IP address (or COM port number) to be
found automatically once the device is connected to the network. For more details, see the chapter below on using
the “
OphirEthernetApp”
software.
Changing to Dynamic IP Address Allocation Mode:
The EA-1 Ethernet Adapter provides the option to use Dynamic IP Address allocation. When enabled, after the EA-1
powers up it sends a request to the local network requesting a free IP address and other IP settings. Once allocated,
this IP address is used automatically by the device without the user having to take any further steps. As long as the
device is not disconnected from the network, this IP address will be permanently allocated to the device. A user
command can be used to query the device about its IP settings (see command $NP below).
Note:
See further details about DHCP in the section on the $TD command below.





























