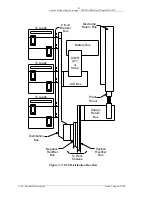
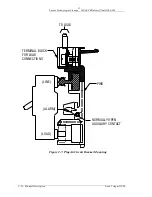
Lucent Technologies Lineage
®
2000 ECS Battery Plant H569-416
Issue 2 August 1996
Engineering, Planning & Ordering 3 - 3
Battery Plant
Voltage
Battery plant operating voltage is directly related to the
recommendations of the battery manufacturer. These
recommendations must include:
•
the steady-state voltage for maximum life or FLOAT
VOLTAGE,
•
the END VOLTAGE after complete discharge,
•
the maximum recharging voltage, and
•
the initial charging method.
EQUALIZE or BOOST charging is recharge capacity greater
than the float voltage.
Rectifier and load equipment voltage ranges are associated with
typical battery voltage ranges. Skip to paragraph “Load Drain
and Growth” for batteryless plants.
A BATTERY STRING consists of a number of battery cells
connected in series to provide the desired plant operating
voltage. This manual deals specifically with NOMINAL 48
VOLT systems, although any plant voltage is possible by
varying the number of cells per string.
The NOMINAL CELL VOLTAGE of lead-acid-type batteries is
usually defined as 2 volts. The actual recommended float voltage
of lead-acid batteries differs slightly among vendors and varies
with chemistry. The most common float voltages are 2.17, 2.27
and 2.35 volts per cell.
Nominal 48 volt systems typically use 23 or 24 cell battery
strings for float voltages that range from 49.91 to 56.40 volts per
string. Lucent Technologies KS-type flooded lead-acid batteries
float at 2.17 volts per cell (52.08 volts per string).
Customers should select a battery type and vendor based on their
maintenance and replacement strategies, initial cost, expected
life, service requirements and replacement cost. Once the battery
is chosen, the following information is needed for the battery
plant engineering process.
f.
Float voltage per cell: ____ volts
g. Minimum cell voltage at end of discharge: ____ volts
h. Is boost or equalize charging recommended?
____ (yes or no)