Installation and operating instructions
IFC 020
2/1
• All operating data and functions can be set: Operation
see Section 4 and 5.7 Function 1.06 and 1.07.
• The pulse and status outputs can be operated in the active or passive mode.
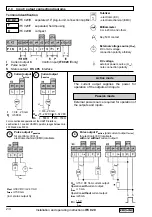
Active mode:
The current output is the internal voltage source,
connection of electronic totalizers (EC)
Passive mode:
External DC or AC voltage source required, connection of electronic (EC)
or electromechanical (EMC) totalizers
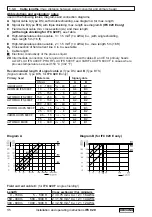
• Digital pulse division, interpulse period is non-uniform. Therefore, if frequency meters or
cycle counters are connected, allow for minimum counting interval:
gate time, counter
≤
1000
P
100%
[ Hz]
•
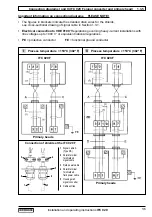
Connection diagrams
see Sect. 2.4: diagrams - pulse output
 Ã
diagrams - status output
Ä Å
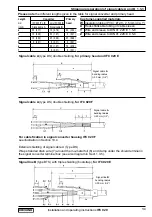
2.1 Current output I
• The current output is galvanically isolated from all input and output circuits.
• Factory-set data and functions can be noted down in Sect. 5.16.
Please also refer to Sect. 3.2 “Factory settings”.
• Typical current output
• All operating data and functions can be set: Operation see Section 4 and 5.6 Function 1.05.
• The current output can also be used as an internal voltage source for the outputs.
U
int
= 15 V DC I = 23 mA when operated
without
receiver instruments at the current output
I = 3 mA when operated
with
receiver instruments at the current output
•
Connection diagrams,
see Sect. 2.4: diagrams
À Á Ã Å
•
For connection and operation with HART
®
-interface see Section 6.1.
I+ approx. 15 V DC positive
voltage of current output
I current sink
I
⊥
chassis ground, current output
2 Electrical connection of outputs and inputs
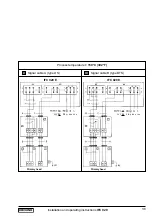
2.2 Pulse output P and status output S
• The pulse and status outputs are galvanically isolated from the current output and all input circuits.
• Factory-set data and functions can be noted down in Sect. 5.16.
Please also refer to Sect. 3.2 “Factory settings”.
• Typical pulse and status outputs
S
status output
P
⊥
⊥
chassis ground
P
pulse output