30
DME1600
Trigger Commands
The DME1600 offers a variety of different trigger oper-
ations. For each individual measurement function, you
can set the trigger mode, trigger source, and trigger
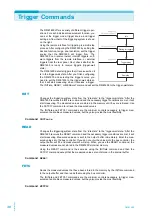
settings. A flow chart of the triggering system is shown
on the right.
Using the remote interface for triggering is a multi-step
process. After configuring the DME1600 by setting the
desired function, range, and resolution, set the trigger
source that the DME1600 will trigger from. The
DME1600 can receive instant internal triggers, soft-
ware triggers from the remote interface, or external
triggers from the rear panel. Next, check whether the
DME1600 is ready to receive triggers (trigger-wait
state).
The DME1600 detects triggers that it receives when it
is in the trigger-wait state. After you finish configuring
the DME1600 and selecting the trigger source, you
need to set the DME1600 to the trigger-wait state so
that it will start measuring when it receives a trigger.
The INITiate, READ?, or MEASure? command will set the DME1600 to the trigger-wait state.
INIT
Changes the triggering system state from the “idle state” to the “trigger-wait state.” After the
DME1600 receives the INITiate command and the necessary trigger conditions are met, it will
start measuring. The measured values are stored in the memory until they are retrieved. Use
the FETCh? command to retrieve the measured values.
The INITiate and FETCh? commands are the minimum controls necessary to trigger mea-
surement and retrieve measured values, but they also provide the most flexibility.
Command
INITiate
READ
Changes the triggering system state from the “idle state” to the “trigger-wait state.” After the
DME1600 receives the READ? command and the necessary trigger conditions are met, it will
start measuring. Measured values are sent to the output buffer immediately. Enter the mea-
sured values into the bus controller. If you do not enter the values into the bus controller, the
output buffer will fill, and measurement will stop. When you use the READ? command, the
measured values are not stored in the DME1600’s internal memory.
Using the READ? command is the same as using the INITiate command and then the
FETCh? command except that the measured values are not stored in the internal buffer.
Command
READ?
FETC
Sends the measured values that have been stored in the memory by the INITiate command
to the output buffer and then reads them using the bus controller.
The INITiate and FETCh? commands are the minimum controls necessary to trigger mea-
surement and retrieve measured values, but they also provide the most flexibility.
Command
FETCh?
Waiting for triggers
Trigger delay
Sampling
Idle
Sample=1
TRIGger:COUNt=1
TRIGger:COUNt≠1
Sample≠1
Summary of Contents for DME1600
Page 4: ...4 DME1600 This page left blank intentionally...
Page 5: ...Setup This chapter explains the settings that you need to configure to use the interfaces 1...
Page 9: ...Message Reference This chapter explains the SCPI com mands 2 Message Reference...
Page 43: ...Appendix A Error Messages B Sample Programs...
Page 55: ......