eSpace 6805 IP Phone
Administrator Guide
6 Appendix
Issue 01 (2014-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
130
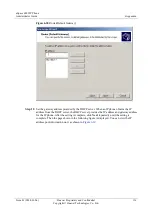
Filter Expression Rules
The Wireshark uses simple expressions to implement the powerful filtering function. A user
can specify the source IP address, destination IP address, and packet field contained in a
protocol or packet, or combine any of the preceding filter criteria. The Wireshark supports
various logical operations, such as
==
,
!=
,
>
,
<
,
and
,
or
,
not
.
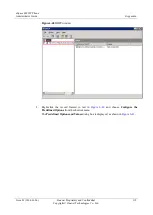
Comparison Symbols
The Wireshark can use comparison symbols (English words or operators) to form filter
expressions.
describes the comparison symbols used in filter expressions.
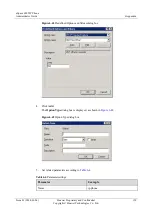
Table 6-6
Comparison symbols used in filter expressions
English
Operator
Description and Setting
eq
==
Equal to
ip.addr==10.138.21.5
ip.addr eq 10.138.21.5
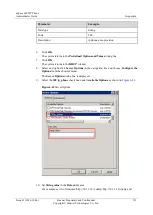
ne
!=
Not equal to
!(ip.addr == 10.138.21.5)
!(ip.addr eq 10.138.21.5)
gt
>
Greater than
frame.pkt_len > 10
frame.pkt_len gt 10
lt
<
Smaller than
frame.pkt_len < 128
frame.pkt_len lt 128
ge
>=
Equal to or greater than
frame.pkt_len >= 0x100
frame.pkt_len ge 0x100
le
<=
Smaller than or equal to
frame.pkt_len <= 0x20
frame.pkt_len le 0x20
Logical Operators
The Wireshark can use logical operators to combine multiple filter expressions. For example,
if you want to filter out packets that are transmitted using the GPRS tunneling protocol (GTP)
and through the IP address 10.138.21.5, use the filter expression gtp &&
ip.addr==10.138.21.5.