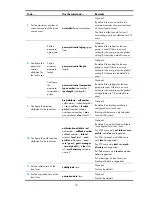
3
Figure 3
Basic RADIUS message exchange process
RADIUS client
RADIUS server
1) Username and password
3) Access-Accept/Reject
2) Access-Request
4) Accounting-Request (start)
5) Accounting-Response
7) Accounting-Request (stop)
8) Accounting-Response
9) Notification of access termination
Host
6) The host accesses the resources
RADIUS operates in the following manner:
1.
The host initiates a connection request that carries the user’s username and password to the
RADIUS client.
2.
Having received the username and password, the RADIUS client sends an authentication request
(Access-Request) to the RADIUS server, with the user password encrypted by using the MD5
algorithm and the shared key.
3.
The RADIUS server authenticates the username and password. If the authentication succeeds, the
server sends back an Access-Accept message containing the user’s authorization information. If the
authentication fails, the server returns an Access-Reject message.
4.
The RADIUS client permits or denies the user according to the returned authentication result. If it
permits the user, it sends a start-accounting request (Accounting-Request) to the RADIUS server.
5.
The RADIUS server returns a start-accounting response (Accounting-Response) and starts
accounting.
6.
The user accesses the network resources.
7.
The host requests the RADIUS client to tear down the connection, and the RADIUS client sends a
stop-accounting request (Accounting-Request) to the RADIUS server.
8.
The RADIUS server returns a stop-accounting response (Accounting-Response) and stops accounting
for the user.
9.
The user stops access to network resources.
RADIUS packet format
RADIUS uses UDP to transmit messages. To ensure smooth message exchange between the RADIUS
server and the client, RADIUS uses a series of mechanisms, including the timer management mechanism,
the retransmission mechanism, and the backup server mechanism.
shows the RADIUS packet
format.