EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
CAGE CODE: 97896
SCALE: NONE SIZE: A
DWG NO.: 060-4199-180
REV: G
SHEET 27 of 68
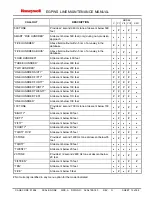
3.4.1 CURRENT FAULTS - INTERNAL
An internal fault indicates a problem with the EGPWC. The following table lists the internal fault messages and the
probable maintenance response.
Note: “NO FAULTS” is enunciated for Level 2 Self-Test if no faults are present.
TABLE 3-2: LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST - INTERNAL FAULTS
Enunciation:
ROM FAILED
RAM FAILED
NVM RAM FAILED
NVM FAILED
WATCHDOG TIMER TEST FAILED
EXCESSIVE WATCHDOG TIMEOUTS FAILURE
ANALOG CONVERTER FAILED*
VOICE GENERATOR FAILED
ARINC 429 TRANSMITTER FAILED
ARINC 429 RECEIVER FAILED
FLASH FILE SYSTEM WRITE FAILED (fixed by MK VI, VIII, XXII Hardware Mod 2)
APPLICATION DATABASE FAILED (DSP or CRC)
TERRAIN DATABASE FAILED (CRC or Runway or Mag. Var.)***
TERRAIN DATABASE NOT COMPATIBLE
ENVELOPE MODULATION DATABASE FAILED
CONFIGURATION DATABASE FAILED (MK V/VII)
APPLICATION DATABASE FAILED (MK VI/VIII/XXII )
CONFIGURATION DATABASE AAC DATA FAULT
SYSTEM OR MODE TASK FAILED
SUPPORT TASK FAILED
INTERNAL GPS FAILED**
APPLICATION SOFTWARE VERSION INVALID
RCD FAILED (MK V/VII)
Probable Cause:
EGPWC failure
Action:
Remove and replace the EGPWC.
Notes
: If external faults also exist, these should be eliminated, and the internal faults rechecked before the EGPWC
is removed and replaced.
* Power unit on bench with parity pin strapped, and verify the failure is cleared.
** If the EGPWC incorporates the integral Mercury GNSSU (-060 hardware part numbers), both internal and
external faults will be indicated. This fault can also be indicated if there is no antenna connection to the GNSSU.
Before replacing the EGPWC/GNSSU, ensure that the antenna is connected and that no antenna wiring breaks
exist.
*** Invalid Latitude/Longitude causes a Mag Var table fault which may be annunciated as “Terrain Database Failed”
This can be caused by not connecting the GPS antenna.
3.4.2 CURRENT FAULTS - EXTERNAL
An external fault indicates a problem with an external sensor, system, or wiring. External faults are further broken
down in to sub-categories; Discrete Faults, ARINC 429 Bus Activity Faults, Analog Input Wire Monitoring Faults,
ARINC 429 Signal Faults, Analog Signal Faults, and Program Pin or Configuration Module Faults. The following
table provides a few examples of these.