EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
CAGE CODE: 97896
SCALE: NONE SIZE: A
DWG NO.: 060-4199-180
REV: G
SHEET 11 of 68
2.1.1 ENHANCED GROUND PROXIMITY WARNING COMPUTER (EGPWC)
All EGPWS functions are processed by a single Line Replaceable Unit (LRU) called the Enhanced Ground
Proximity Warning Computer (EGPWC).
The MK V and MK VII EGPWC are digitally controlled computers housed in a 2 MCU ARINC 600-6 form factor
chassis intended for Air Transport type aircraft. Installation configuration is defined by program pin strapping in the
aircraft.
The MK VI and MK VIII EGPWC are digitally controlled computers housed in a non-ARINC form factor chassis
intended for Business and General Aviation and Regional Turboprop type aircraft. These models have fewer
interface and functional options. The installation configuration is defined in a programmed Configuration Module
installed in the aircraft.
The MK XXII EGPWC is a digitally controlled computer housed in a non-ARINC form factor chassis intended for
various rotorcraft. Similar to the MK VI and MK VIII EGPWC, this model has fewer interface and functional options.
The installation configuration is defined in a programmed Configuration Module installed in the helicopter.
The EGPWC receives information in AC, DC, discrete, and synchro analog formats, and RS-232, RS-422, ARINC
429 or ARINC 575 digital formats. Discrete signals can be either ground or +28V discretes. The EGPWC provides
discrete, audio and ARINC 429 outputs for alerts and system status, and video (ARINC 453/708) for terrain display.
The EGPWC is rack mounted and does not require any forced air cooling when operated within the normal
operating temperature range given in the Table 1-1.
2.2 OPERATION
2.2.1 MODE 1 – EXCESSIVE DESCENT RATE
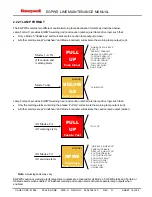
Mode 1 provides audio and visual alerts for excessive descent rates into terrain. When the EGPWS caution alert
envelope is penetrated, the message “SINKRATE” is enunciated and EGPWS alert lights illuminate. Continuing the
excessive descent rate into the EGPWS warning alert envelope results in a “PULL-UP” enunciation and EGPWS
alert lights illuminated. Mode 1 is desensitized to eliminate unwanted (nuisance) alerts when the EGPWS
determines that the aircraft is above a Glideslope beam. In some fixed-wing applications, Mode 1 is also
desensitized when Steep Approach or Flap Override is active. In helicopter applications, Mode 1 is disabled when
autorotation is detected.
2.2.2 MODE 2A/2B - TERRAIN CLOSURE RATE
Mode 2 provides audio and visual alerts for dangerously high terrain closure rates. Two sub-modes, referred to as
Mode 2A and 2B, are defined. Mode 2A is active when flaps are not in the landing position and the aircraft is not on
an ILS approach within ± 2 dots of glideslope center. Mode 2B is active when the flaps are in the landing position or
while on an ILS approach within ± 2 dots of glideslope deviation. When the caution alert envelope is penetrated, the
message “TERRAIN, TERRAIN” is enunciated and EGPWS alert lights illuminate. Continuing the high terrain
closure rate into the warning alert envelope results in a “PULL-UP” enunciation and EGPWS alert lights illuminated.
2.2.3 MODE 3 - DESCENT AFTER TAKEOFF
Mode 3 provides audio and visual alerts for excessive altitude loss after takeoff, or after a go-around from below 245
feet above ground level (AGL), when flaps and gear are not in the landing configuration. Penetrating the Mode 3
alert envelope causes the voice message “DON’T SINK, DON’T SINK” and illumination of EGPWS alert lights.
2.2.4 MODE 4A/4B/4C - UNSAFE TERRAIN CLEARANCE
Mode 4 provides audio and visual alerts for unsafe terrain clearance with respect to phase of flight, height above
ground, and speed. Three sub-modes, referred to as Mode 4A, 4B, and 4C, are defined. Mode 4A is active during
cruise and approach with landing gear up. Mode 4B is active during cruise and approach with landing gear down
and flaps up. Mode 4C is active during takeoff when either gear or flaps are not in the landing configuration. The
aural enunciations for Mode 4A are “TOO LOW TERRAIN” or “TOO LOW GEAR” depending on airspeed. Mode 4B