159
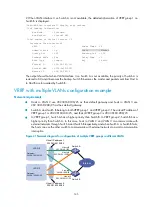
When Switch A fails, you can still ping Host B on Host A. To view the detailed information of the VRRP
group on Switch B, use the
display vrrp ipv6 verbose
command.
# When Switch A fails, the detailed information of VRRP group 1 on Switch B is displayed.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] display vrrp ipv6 verbose
IPv6 Standby Information:
Run Mode : Standard
Run Method : Virtual MAC
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface Vlan-interface2
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 100
Admin Status : Up State : Master
Config Pri : 100 Running Pri : 100
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5
Auth Type : None
Virtual IP : FE80::10
1::10
Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0201
Master IP : FE80::2
The output shows that when Switch A fails, Switch B becomes the master, and packets sent from Host A
to Host B are forwarded by Switch B.
# After Switch A resumes normal operation, use the
display vrrp ipv6
verbose
command to display the
detailed information of VRRP group 1 on Switch A.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] display vrrp ipv6 verbose
IPv6 Standby Information:
Run Mode : Standard
Run Method : Virtual MAC
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface Vlan-interface2
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 100
Admin Status : Up State : Master
Config Pri : 110 Running Pri : 110
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5
Auth Type : None
Virtual IP : FE80::10
1::10
Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0201
Master IP : FE80::1
The output shows that after Switch A resumes normal operation, it becomes the master, and packets sent
from host A to host B are forwarded by Switch A.
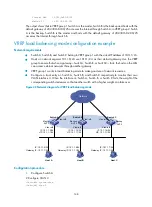
VRRP interface tracking configuration example
Network requirements
•
Switch A and Switch B belong to VRRP group 1 with the virtual IP addresses of 1::10/64 and
FE80::10.
•
Host A wants to access Host B on the Internet, and learns 1::10/64 as its default gateway through
RA messages sent by the switches.