213
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=2 ms
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=2 ms
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=1 ms
--- 30.1.1.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms
# The output on Switch D is similar to that on Switch A. When the master route fails, the hosts in
30.1.1.0/24 can still communicate with the hosts in 20.1.1.0/24.
[SwitchB] ping -a 30.1.1.1 20.1.1.1
PING 20.1.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 20.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=2 ms
Reply from 20.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 20.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 20.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 20.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=1 ms
--- 20.1.1.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms
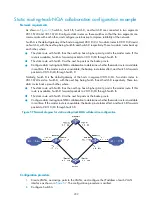
Static routing-track-BFD collaboration configuration example
Network requirements
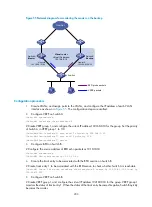
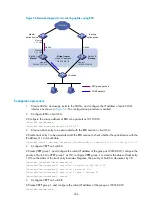
As shown in
, Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C are connected to two segments 20.1.1.0/24
and 30.1.1.0/24. Configure static routes on these routers so that the two segments can communicate with
each other, and configure route backup to improve reliability of the network.
Switch A is the default gateway of the hosts in segment 20.1.1.0/24. Two static routes to 30.1.1.0/24 exist
on Switch A, with the next hop being Switch B and Switch C respectively. These two static routes back up
each other, where:
•
The static route with Switch B as the next hop has a higher priority, and is the master route. If this
route is available, Switch A forwards packets to 30.1.1.0/24 through Switch B.
•
The static route with Switch C as the next hop acts as the backup route.
•
Configure static routing-track-BFD collaboration to determine whether the master route is available
in real time. If the master route is unavailable, BFD can quickly detect the route failure to make the
backup route take effect, and Switch A forwards packets to 30.1.1.0/24 through Switch C and
Switch B.
Similarly, Switch B is the default gateway of the hosts in segment 30.1.1.0/24. Two static routes to
20.1.1.0/24 exist on Switch B, with the next hop being Switch A and Switch C respectively. These two
static routes back up each other, where:
•
The static route with Switch A as the next hop has a higher priority, and is the master route. If this
route is available, Switch B forwards packets to 20.1.1.0/24 through Switch A.
•
The static route with Switch C as the next hop acts as the backup route.