120
•
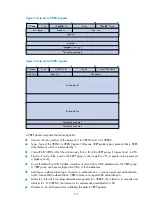
IP Address/IPv6 Address—Virtual IPv4 or IPv6 address entry of the VRRP group. The Count IP Addrs
or Count IPv6 Addrs field defines the number of the virtual IP v4 or IPv6 addresses.
•
Authentication Data—Authentication key. This field is used only for simple authentication and is 0
for any other authentication modes.
Principles of VRRP
•
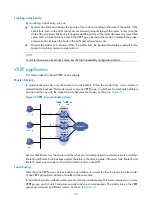
Routers in a VRRP group determine their roles by priority. The router with the highest priority is the
master, and the others are the backups. The master periodically sends VRRP advertisements to notify
the backups that it is working properly, and each of the backups starts a timer to wait for
advertisements from the master.
•
In preemptive mode, when a backup receives a VRRP advertisement, it compares the priority in the
packet with its own priority. If the priority of the backup is higher, the backup becomes the master.
Otherwise, it remains as a backup. In preemptive mode, a VRRP group always has the router with
the highest priority as the master for packet forwarding.
•
In non-preemptive mode, a router in the VRRP group remains as a master or backup as long as the
master does not fail. A backup does not become the master even if it is configured with a higher
priority. The non-preemptive mode helps avoid frequent switchover between the master and
backups.
•
If the timer of a backup expires but the backup still does not receive any VRRP advertisement, it
considers that the master fails. In this case, the backup considers itself as the master and sends VRRP
advertisements to start a new master election.
NOTE:
•
The VRRP group configuration might be different on routers, and network problems might exist, so
multiple master routers might exist in one VRRP group. These master routers will elect one master
according to their priorities and IP addresses. The router with the highest priority wins the election. If a
tie exists in the priority, the router with the highest IP address wins.
•
After a backup router receives an advertisement, it compares its priority against that carried in the
advertisement. If its priority is higher than that carried in the advertisement, it takes over the master.
VRRP tracking
NOTE:
To enable VRRP tracking, configure the routers in the VRRP group to work in preemptive mode first, so that
only the router with the highest priority always operates as the master for packet forwarding.
Tracking a specified interface
The interface tracking function expands the backup functionality of VRRP. It provides backup not only
when the interface to which a VRRP group is assigned fails but also when other interfaces—such as
uplink interfaces—on the router become unavailable.
•
If the uplink interface of a router in a VRRP group fails, usually the VRRP group cannot be aware of
the uplink interface failure. If the router is the master of the VRRP group, hosts on the LAN are not
able to access external networks because of the uplink failure. This problem can be solved by
tracking a specified uplink interface. If the tracked uplink interface is down or removed, the priority
of the master is automatically decreased by a specified value. A higher priority router in the VRRP
group becomes the master.