8
DNP 3.0
This section describes how the DNP 3.0 standard is applied to the Px40 platform. It is not a description of the
standard itself. The level at which this section is written assumes that the reader is already familiar with the
DNP 3.0 standard.
The descriptions given here are intended to accompany the device profile document that is included in the
Menu Database document. The DNP 3.0 protocol is not described here, please refer to the documentation
available from the user group. The device profile document specifies the full details of the DNP 3.0
implementation. This is the standard format DNP 3.0 document that specifies which objects; variations and
qualifiers are supported. The device profile document also specifies what data is available from the device
using DNP 3.0. The IED operates as a DNP 3.0 slave and supports subset level 2, as described in the
DNP 3.0 standard, plus some of the features from level 3.
The DNP 3.0 protocol is defined and administered by the DNP Users Group. For further information on
DNP 3.0 and the protocol specifications, please see the DNP website (www.dnp.org).
8.1
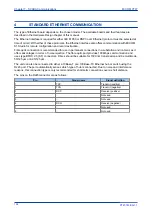
PHYSICAL CONNECTION AND LINK LAYER
DNP 3.0 can be used with three physical layer protocols: EIA(RS)232, EIA(RS)485, or Ethernet.
Several connection options are available for DNP 3.0
●
Rear Port 1 (RP1) - for permanent SCADA connection via RS485
●
Optional fibre port (RP1 in slot A) - for permanent SCADA connection via optical fibre
●
Optional Rear Port 2 (RP2) - for permanent SCADA connection via RS485 or RS232
●
An RJ45 connection on an optional Ethernet board - for permanent SCADA Ethernet connection
●
A fibre connection on an optional Ethernet board - for permanent SCADA Ethernet connection
The IED address and baud rate can be selected using the front panel menu or by the settings application
software.
When using a serial interface, the data format is: 1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and optional configurable
parity bit.
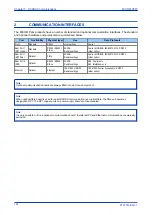
8.2
OBJECT 1 BINARY INPUTS
Object 1, binary inputs, contains information describing the state of signals in the IED, which mostly form part
of the digital data bus (DDB). In general these include the state of the output contacts and opto-inputs, alarm
signals, and protection start and trip signals. The ‘DDB number’ column in the device profile document
provides the DDB numbers for the DNP 3.0 point data. These can be used to cross-reference to the DDB
definition list. See the relevant Menu Database document. The binary input points can also be read as
change events using Object 2 and Object 60 for class 1-3 event data.
8.3
OBJECT 10 BINARY OUTPUTS
Object 10, binary outputs, contains commands that can be operated using DNP 3.0. Therefore the points
accept commands of type pulse on (null, trip, close) and latch on/off as detailed in the device profile in the
relevant Menu Database document, and execute the command once for either command. The other fields
are ignored (queue, clear, trip/close, in time and off time).
There is an additional image of the Control Inputs. Described as Alias Control Inputs, they reflect the state of
the Control Input, but with a dynamic nature.
●
If the Control Input DDB signal is already SET and a new DNP SET command is sent to the Control
Input, the Control Input DDB signal goes momentarily to RESET and then back to SET.
●
If the Control Input DDB signal is already RESET and a new DNP RESET command is sent to the
Control Input, the Control Input DDB signal goes momentarily to SET and then back to RESET.
MiCOM P747
Chapter 7 - SCADA Communications
P747-TM-EN-1
207
P747-TM-EN-1.1
Summary of Contents for MiCOM P747 Agile
Page 2: ......
Page 16: ...Contents MiCOM P747 xiv P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 20: ...Table of Figures MiCOM P747 xviii P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 21: ...INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1...
Page 22: ...Chapter 1 Introduction MiCOM P747 2 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 31: ...SAFETY INFORMATION CHAPTER 2...
Page 32: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information MiCOM P747 12 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 42: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information MiCOM P747 22 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 43: ...HARDWARE DESIGN CHAPTER 3...
Page 44: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design MiCOM P747 24 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 74: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design MiCOM P747 54 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 75: ...CONFIGURATION CHAPTER 4...
Page 76: ...Chapter 4 Configuration MiCOM P747 56 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 117: ...PROTECTION FUNCTIONS CHAPTER 5...
Page 118: ...Chapter 5 Protection Functions MiCOM P747 98 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 160: ...Chapter 5 Protection Functions MiCOM P747 140 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 161: ...MONITORING AND CONTROL CHAPTER 6...
Page 162: ...Chapter 6 Monitoring and Control MiCOM P747 142 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 211: ...SCADA COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 7...
Page 212: ...Chapter 7 SCADA Communications MiCOM P747 192 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 259: ...REDUNDANT ETHERNET CHAPTER 8...
Page 260: ...Chapter 8 Redundant Ethernet MiCOM P747 240 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 293: ...CYBER SECURITY CHAPTER 9...
Page 294: ...Chapter 9 Cyber Security MiCOM P747 274 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 313: ...SETTINGS APPLICATION SOFTWARE CHAPTER 10...
Page 314: ...Chapter 10 Settings Application Software MiCOM P747 294 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 322: ...Chapter 10 Settings Application Software MiCOM P747 302 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 323: ...BUSBAR COMMISSIONING TOOL CHAPTER 11...
Page 324: ...Chapter 11 Busbar Commissioning Tool MiCOM P747 304 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 330: ...Chapter 11 Busbar Commissioning Tool MiCOM P747 310 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 331: ...SCHEME LOGIC CHAPTER 12...
Page 332: ...Chapter 12 Scheme Logic MiCOM P747 312 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 348: ...Chapter 12 Scheme Logic MiCOM P747 328 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 349: ...INSTALLATION CHAPTER 13...
Page 350: ...Chapter 13 Installation MiCOM P747 330 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 361: ...COMMISSIONING INSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 14...
Page 362: ...Chapter 14 Commissioning Instructions MiCOM P747 342 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 387: ...MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING CHAPTER 15...
Page 388: ...Chapter 15 Maintenance and Troubleshooting MiCOM P747 368 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 403: ...TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 16...
Page 404: ...Chapter 16 Technical Specifications MiCOM P747 384 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 425: ...SYMBOLS AND GLOSSARY APPENDIX A...
Page 426: ...Appendix A Symbols and Glossary MiCOM P747 406 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 443: ...COMMISSIONING RECORD APPENDIX B...
Page 444: ...Appendix B Commissioning Record MiCOM P747 424 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 449: ...WIRING DIAGRAMS APPENDIX C...
Page 450: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams MiCOM P747 430 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 456: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams MiCOM P747 436 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 457: ......