Product variant
Supported protocol
CMMTAS...EC
EtherCAT
CMMTAS...EP
EtherNet/IP
CMMTAS...PN
PROFINET
Tab. 28 Supported protocol
The physical level of the interface fulfils the requirements according to IEEE 802.3.
The interface is electrically isolated and intended for use with limited cable
lengths
è
Tab. 29 Requirements for the connecting cable.
The interface [X19] offers 2 ports.
–
Port 1, labelled on the device with [X19, XF1 IN]
–
Port 2, labelled on the device with [X19, XF2 OUT]
2 LEDs are integrated into each of the two RJ45 bushings. The behaviour of the
LEDs depends on the bus protocol. Use is not always made of both LEDs.
Requirements for the connecting cable
Characteristics
CAT 5, patch cable, double shielded
Max. cable length
30 m
Tab. 29 Requirements for the connecting cable
8.9
Motor connection
8.9.1
[X6A], Motor phase connection
The connection [X6A] is located on the front of the device. The following connec
tions to the motor are established via the connection [X6A]:
–
Motor phases U, V, W
–
PE connection
[X6A]
Pin
Function
Description
4
PE
Protective earth, motor
3
W
Third motor phase
2
V
Second motor phase
1
U
First motor phase
Tab. 30 Motor phase connection
The cable shield of the motor cable must be placed on the support surface on the
bottom front of the housing and fastened with the shield clamp.
Requirements for the connecting cable
Wires and shielding
–
4 power wires, shielded
–
Extra optional cables, e.g. for the holding
brake (shielded separately) and the motor
temperature sensor (shielded separately)
Design
Only use cables that ensure safe separation
between the motor phases and the shielded sig
nals of the holding brake and motor temperature
sensor.
è
8.9.4 Shield support of the motor cable
Max. cable length
è
8.6 Information on EMCcompliant installation
Max. capacitance
<
250 pF/m
Nominal cross section of power wires
0.75 mm
2
… 1.5 mm²
Cable diameter of the stripped cable or shield
sleeve (clamping range of the shield clamp)
11 mm … 15 mm
The only motor cables permitted are those that fulfil the requirements of EN 6180052 Annex D.3.1
and the requirements of EN 602041.
For cUL, only use Cu cables that have a permissible constant insulation temperature of at least
75 °C.
Tab. 31 Requirements for the connecting cable
Festo offers prefabricated motor cables as accessories
è
www.festo.com/catalogue.
–
Only use motor cables that have been approved for operation with the Festo
servo drive. Motor cables of other manufacturers are permitted if they meet
the specified requirements.
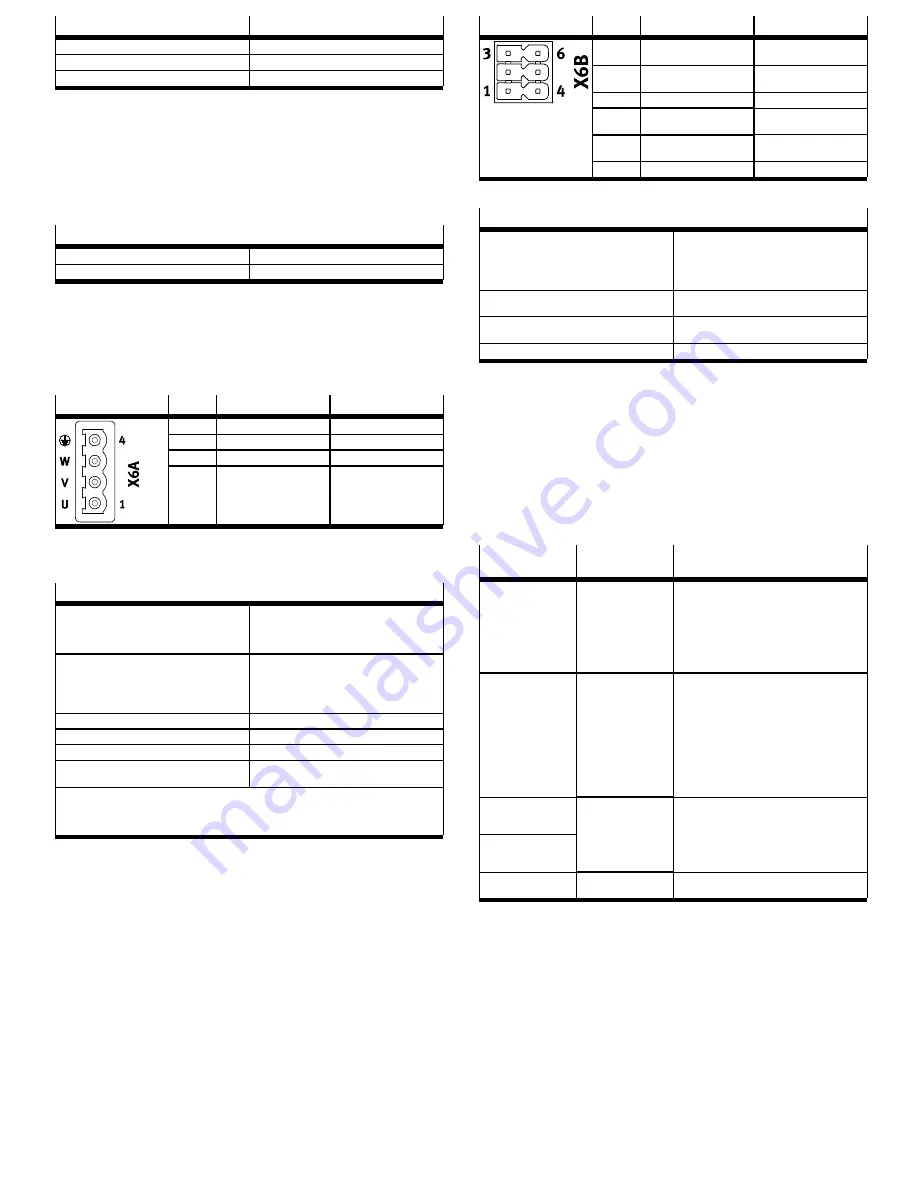
8.9.2
[X6B], Motor auxiliary connection
The connection [X6B] is located on the front of the device. The holding brake of
the motor and the motor temperature sensor can be connected to the connection
[X6B]. The output for the holding brake is used both functionally and in connec
tion with the safety subfunction Safe brake control
è
Description Safety sub
function.
To allow motor temperature monitoring, the following are supported:
–
N/C and N/O contacts
–
KTY 81 … 84 (silicon temperature sensors)
–
PTC (positive temperature coefficient)
–
NTC (negative temperature coefficient)
–
Pt1000 (platinum measuring resistor)
The servo drive monitors whether the motor temperature violates an upper or
lower limit. With switching sensors, only the upper limit value can be monitored
(e.g. with a normally closed contact). The limit values and the error reactions can
be parameterised.
[X6B]
Pin
Function
Description
6
MT–
Motor temperature (negat
ive potential)
5
MT+
Motor temperature (posit
ive potential)
4
PE
Protective earthing
3
BR–
Holding brake (negative
potential)
2
BR+
Holding brake (positive
potential)
1
PE
Protective earthing
Tab. 32 Motor auxiliary connection
Requirements for the connecting cable
Design
–
2 wires for the line to the holding brake,
twisted in pairs, separately shielded
–
2 wires for the line to the temperature
sensor, twisted in pairs, separately shiel
ded
Min. conductor cross section including cable end
sleeve with plastic sleeve
0.25 mm
2
Max. conductor cross section including cable end
sleeve with plastic sleeve
0.75 mm
2
Max. length
50 m
1)
1) With cable lengths
>
25 m, take account of the voltage drop on the cables by selecting appropriate wire
cross sections.
Tab. 33 Requirements for the connecting cable
Requirement for the temperature sensor in the motor
–
Electrically safe separation from the motor phases in accordance with
IEC 6180051, voltage class C, overvoltage category III.
Shield connection requirements
–
Make unshielded cable ends as short as possible (max. 150 mm).
–
Connect the cable shield on both sides.
8.9.3
Electronic overload and overtemperature protection for the motor
The CMMTAS allows the motor to be electronically protected against overload
and overtemperature by offering the following protective functions:
Protective func-
tions
Description
Measures required during installation
and commissioning
Temperature monitor
ing of the motor
The motor temperature
is monitored for an
upper and lower limit
value, including hyster
esis. The limit values
can be parameterised.
–
Connect temperature sensor to connection
[X6B] (both switching and analogue temper
ature sensors are supported)
–
Parameterise temperature limit values in
accordance with type of motor used,
e.g. using the devicespecific plugin.
Respect the permissible limit values of the
motor.
Electronic current limit
ing and I²t monitoring
of the motor current
The motor current is
monitored electronic
ally and limited in
accordance with the
limit values specified
by standard
è
EN 6180051, Tab.
29.
Motor currents and I²t
time constant can be
parameterised.
–
Parameterise nominal current, maximum
current and I²t time constant of the motor,
e.g. using the devicespecific plugin.
Thermal memory in the
event of motor switch
off
Thermal memory in the
event of a power sup
ply failure
Supported, cannot be
parameterised
None
Speedsensitive over
load protection
Not supported
—
Tab. 34 Protective functions for the motor
The specified parameters are preset for Festo motors. The parameters can be
adjusted via the plugin on parameter page Axis 1/Motor.
8.9.4
Shield support of the motor cable
Requirements for connecting the motor cable shield on the device side
The type of shield connection depends on the design of the motor cable. If,
for example, a hybrid cable is used to connect the motor, holding brake, and tem
perature sensor, the following options exist for connecting the shield on the
device side:
Option 1: All motor cable shields are jointly connected over a large surface area
using a shield sleeve at the cable end and are connected below the shield clamp
on the front of the CMMTAS.


































