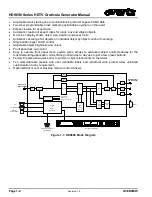
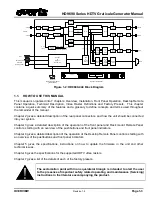
HD9690 Series HDTV Graticule Generator Manual
OVERVIEW
Revision 1.5
Page 1-5
CLIFF EFFECT:
(also referred to as the ‘digital cliff’) This is a phenomenon found in digital video systems
that describes the sudden deterioration of picture quality due to excessive bit errors, often
caused by excessive cable lengths. The digital signal will be perfect even though one of its
signal parameters is approaching or passing the specified limits. At a given moment, however,
the parameter will reach a point where the data can no longer be interpreted correctly and the
picture will become totally unrecognisable.
COMPONENT ANALOG:
The non-encoded output of a camera, video tape recorder, etc., consisting of
the three primary colour signals: red, green, and blue (RGB) that together convey all necessary
picture information. In some component video formats these three components have been
translated into a luminance signal and two colour difference signals. For example: Y, B-Y, R-Y
or more commonly referred to as YPbPr.
COMPONENT DIGITAL:
A digital representation of a component analog signal set in either RGB or
Y, B-Y, R-Y (or more commonly referred to as YcbCr) format The encoding parameters for HD
component video are specified by ITU-R Rec 709. SMPTE 274M and SMPTE 296M specify
the parallel interface. SMPTE ST 292-1 specifies the serial interface for 4:2:2 sampled signals
and SMPTE ST 372 specifies the serial interface for 4:4:4 samples signals.
EAV:
Abbreviation for "End of Active Video". A digital synchronization sequence consisting of a
sequence of four consecutive code words (a code word of all ones, a code word of all zeros,
another code word of all zeros, and a code word including F (field/frame), V (vertical), H
(horizontal), P3, P2, P1, and P0 (parity) bits.) which is used to designate the start of the
horizontal blanking interval of the digital line. See also SAV.
EBU (European Broadcasting Union):
An organization of European broadcasters that, among other
activities, provides technical recommendations for the 50 hz television systems.
EMBEDDED AUDIO:
Digital audio is multiplexed onto the high definition serial digital video bit stream
according to the SMPTE 299M standard.
FSRGB
Full Scale RGB, also known as
extended range RGB
. In high definition extended range RGB
digital video, the three primary components are scaled such that the extreme values are code
words 04
h
(4) and 3FB
h
(1019) in a 10-bit representation. See also RGB.
HDSDI
An abbreviation for
high definition serial digital interface
, this acronym is most commonly used
to refer to high definition serial digital television video signals at 1.485 Gb/s.
HDTV
An abbreviation for
high definition television
, this acronym is most commonly used to refer to
High definition serial digital television video signals at 1.485 Gb/s.
HEXADECIMAL
Also abbreviated as
HEX.
Refers to the base-16 number system, which consists of
16 unique symbols: the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. Throughout this manual
hexadecimal numbers will be denoted by an
h
suffix. For example, the decimal number 15 is
represented as F
h
. The hexadecimal system is useful
because it can represent every byte (8 bits) as two consecutive hexadecimal digits. It is easier
for humans to read hexadecimal numbers than binary numbers. To convert a value from
hexadecimal to binary, you merely translate each hexadecimal digit into its 4-bit binary
equivalent. For example, the hexadecimal number 3F7A
h
translates to the binary number:
0011 1111 0111 1010.