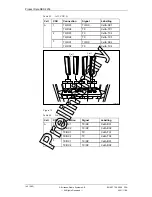
Unit Description, dTRU
•
CPU-system
•
DSP-system
•
RC-system
•
Radio system
CPU System
The CPU system is a control unit in the RBS. Basically it consists of a
CPU, support logic, memory and logic for handling the interfaces.
DSP System
The DSP system performs all baseband signal processing necessary for
one TRX. For downlink, this includes Terrestrial Protocol Handling
(TPH), encoding, ciphering and burst generation. For uplink it includes
equalization, combining, decoding and TPH.
RC System
The Radio Control system is responsible for synchronizing and
controlling the different parts of the radio, for modulation and D/A
conversion of the data to transmit, for filtering the received radio signal
with a channel selective filter and for compensating the receiver and
transmitter delays and gain variations.
The Radio Control system is seen by the rest of the RBS as the front
end to the radio which can be asked to transmit a burst of data using a
selected modulation, or asked to receive a burst using a selected digital
filter.
All the time critical radio control functions are performed by the Radio
Control system and no computing support is required from the CPU
system on a real time basis.
Radio System
Each Radio system contains two radio receivers and one radio
transmitter including power amplifiers.
The radio receiver receives RF modulated uplink data from one or two
diversity branches and sends it to the Radio Control system.
The radio transmitter generates the RF downlink signal from the
modulated baseband signal. It then sends the RF signal to the power
amplifier which amplifies the downlink RF signals.
8.2
Functions
The dTRU serves as a distributed main CPU DMCN and its main
functions are:
•
Transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals – GMSK or
8-PSK modulation
•
Signal processing
156 (485)
EN/LZT 720 0008
P2A
2001-11-28
© Ericsson Radio Systems AB
— All Rights Reserved —
P
re
li
m
in
a
ry
Summary of Contents for RBS 2106
Page 2: ...P r e l i m i n a r y ...