30
Enertech Global
IOM, BS/BT Models
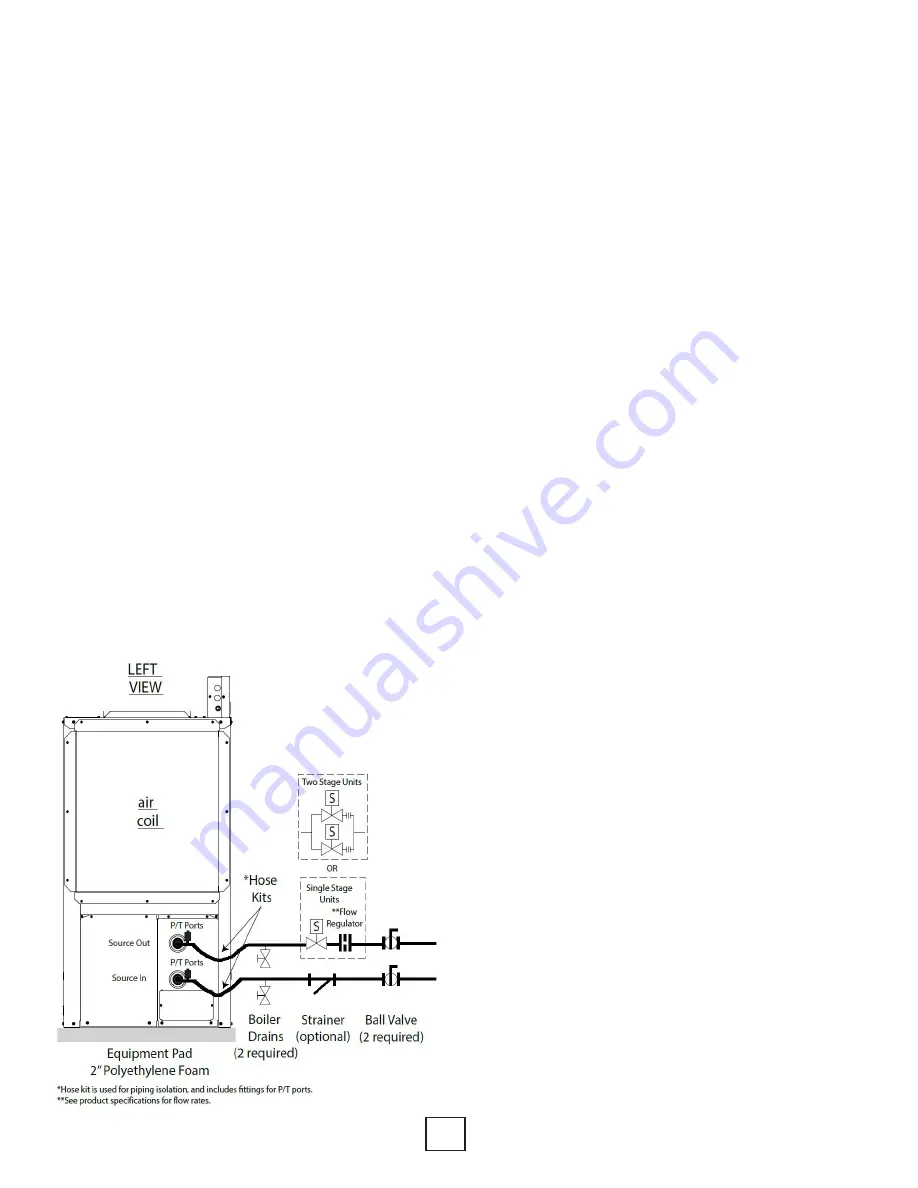
Open Loop Piping
Placement of components for an open loop system
is important when considering water quality and
long term maintenance. The water solenoid valve
should always be placed on the outlet of the heat
pump, which will keep the heat exchanger under
pressure when the unit is not operating. If the heat
exchanger is under pressure, minerals will stay
in suspension. Water solenoid valves are also
designed to close against the pressure, not with the
pressure. Otherwise, they tend to be noisy when
closing.
A flow regulator should be placed after the
water solenoid valve. Always check the product
specification catalog for proper flow rate. A
calculation must be made to determine the flow rate,
so that the leaving water temperature does not have
the possibility of freezing.
Note:
Model shown in drawing reflects typical
connection locations. Your model may have different
connection locations. Please identify correct input
and output port locations.
Figure 15: Open Loop Piping Example
Drawings represent typical unit installation.
Connection location, type and appearance may
differ per model.
Section 6: Unit Piping Installation
Other necessary components include a strainer,
boiler drains for heat exchanger flushing, P/T ports
and ball valves. Ball valves allow the water to be
shut off for service, and also help when velocity
noise is noticeable through the flow regulator.
Spreading some of the pressure drop across the
ball valves will lessen the velocity noise. Always
double check flow rate at the P/T ports to make
sure the ball valve adjustments have not lowered
water flow too much, and essentially taken the flow
regulator out of the equation. It’s a good idea to
remove the ball valve handles once the system is
completed to avoid nuisance service calls.
Hose kits are recommended and make for an easier
installation, since the P/T ports and connections are
included. The hose also helps to isolate the heat
pump from the piping system.
Since the heat pump can operate at lower water
flow on first stage, two stage units typically include
two water solenoid valves to save water. The flow
regulators should be sized so that when one valve
is open the unit operates at first stage flow rate,
and when both valves are open, the unit operates
at full load flow rate. For example, a 4 ton unit
needs approximately 4 GPM on first stage, and
approximately 7 GPM at full load. The flow regulator
after the first valve should be 4 GPM, and the flow
regulator after the second valve should be 3 GPM.
When both valves are open, the unit will operate at
7 GPM.
Two-stage solenoid example is optional for all sizes.
It is not recommended for 3 ton and smaller. Use
single solenoid and flow regulator.






























