PMAC Quick Reference Guide
54
Motion Programs
Starting point
i (inc)
j (inc)
X (inc)
Y (inc)
End point
Center
Starting point
j
i (abs)
Y
X (abs)
Center
0,0
End point
Y
X
Z
k-1
X
X
Y Y
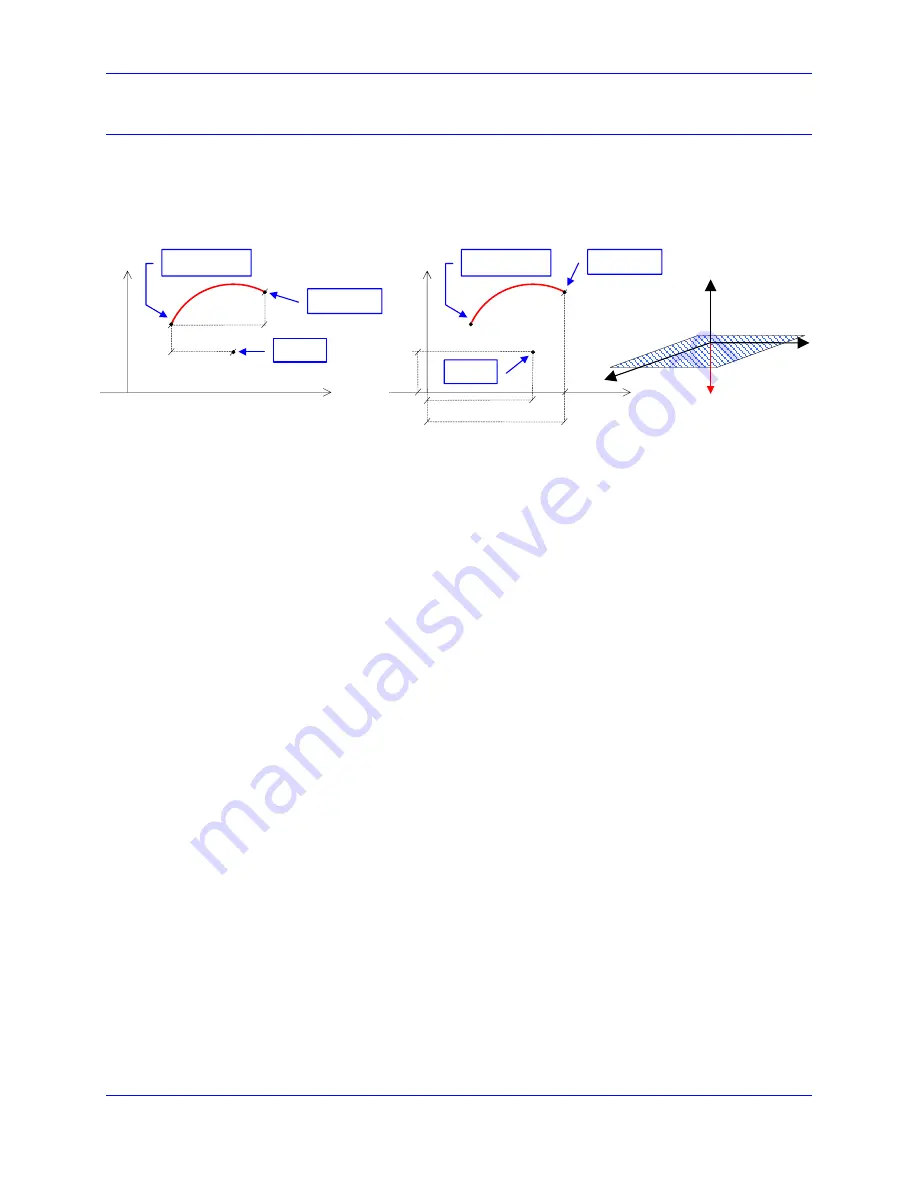
Circular Interpolation
PMAC allows circular interpolation on the X, Y, and Z-axes in a coordinate system. As with linear
blended moves, TA and TS control the acceleration to and from a stop, and between moves. Circular
blended moves can be feedrate-specified (
F
) or time-specified (
TM
), just as with linear moves. It is
possible to change back and forth between linear and circular moves without stopping. When linear
interpolation is needed, enter the
LINEAR
command and Circle1
or Circle2
for circular interpolation.
1. PMAC performs arc moves by segmenting the arc and performing the best cubic fit on each segment.
I-Variable I13 determines the time for each segment. I13 must be set greater than zero to put PMAC
into this segmentation mode in order for arc moves to be done. If I13 is set to zero, circular arc
moves will be done in linear fashion.
The practical range of I13 for the circular interpolation mode is 5-10 msec. A value of 10 msec is
recommended for most applications, a lower than 10 msec I13 value will improve the accuracy of the
interpolation (calculating points of the curve more often) but will also consume more of PMAC’s
total computational power.
2. When PMAC is segmenting moves (I13 > 0) automatically, which is required for Circular
Interpolation. The Ix17 accelerations limits and the Ix16 velocity limits are not observed.
3. Any axes used in the circular interpolation are automatically feedrate axes for circular moves, even if
they were not so specified in an
FRAX
command. Other axes may or may not be feedrate axes. Any
non-feedrate axes commanded to move in the same move command will be linearly interpolated so as
to finish in the same time. This permits easy helical interpolation.
4. The plane for the circular arc must have been defined by the
NORMAL
command (the default --
NORMAL K-1
-- defines the XY plane). This command can define only planes in XYZ-space, which
means that only the X, Y, and Z axes can be used for circular interpolation. Other axes specified in
the same move command will be interpolated linearly to finish in the same time. The most commonly
used planes are:
NORMAL K-1
; XY plane -- equivalent to G17
NORMAL J-1
; ZX plane -- equivalent to G18
NORMAL I-1
; YZ plane -- equivalent to G19
5. To put the program in circular mode, use the
CIRCLE1
program command for clockwise arcs (G02
equivalent) or
CIRCLE2
for counterclockwise arcs (G03 equivalent).
LINEAR
will restore PMAC to
linear blended moves. Once in circular mode, a circular move is specified with a move command
specifying the move endpoint and either the vector to the arc center or the distance (radius) to the
center. The endpoint may be specified either as a position or as a distance from the starting point,
depending on whether the axes are in absolute (
ABS
) or incremental (
INC
) mode (individually
specifiable).
X{Data} Y{Data} R{Data}
;Radius of the circle is given
X{Data} Y{Data} I{Data} J{Data}
;Center coordinates of the circle are given
Summary of Contents for PMAC Mini
Page 4: ......
Page 8: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide iv Table of Contents ...
Page 28: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide 20 PMAC Executive Program PEWIN ...
Page 80: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide 72 Troubleshooting ...
Page 82: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide 74 Appendix A PMAC Error Code Summary ...
Page 88: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide 80 Appendix B PMAC I Variables Summary ...
Page 106: ...PMAC Quick Reference Guide 98 Appendix F I O Suggested M Variable Definitions ...
















































