VLT
®
FCD Series
NB!:
The minimum brake resistance selected
should have an ohmic value no more than
10% lower than that recommended by Danfoss. If a
lower brake resistance is selected there is a risk of
overcurrent, which can destroy the unit.
■
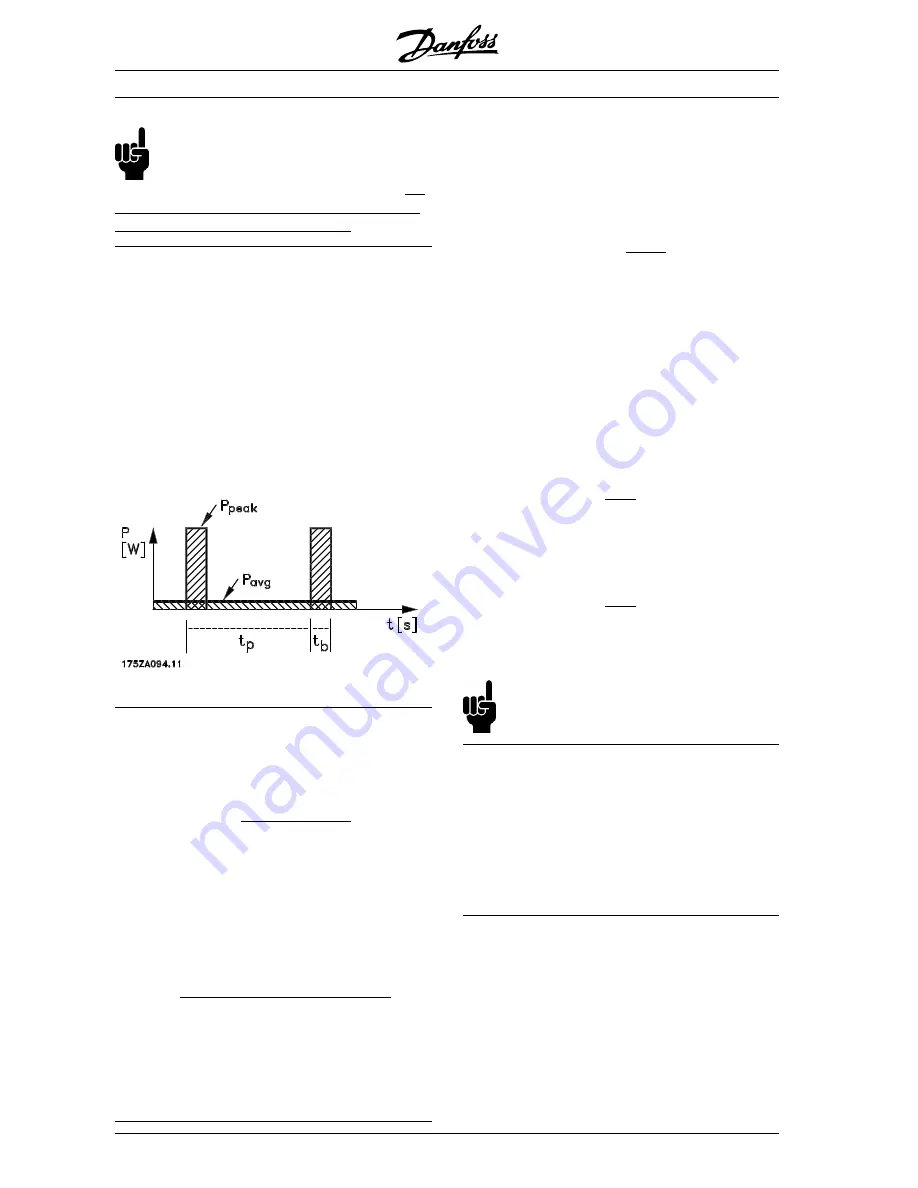
Calculation of braking power
When calculating the braking power, it must be
ensured that the mean and peak powers can be dis-
sipated to the brake resistor. The mean power is
determined by the period time of the process, i.e. for
how long the brake is applied in relation to the
period time of the process. The peak power is deter-
mined by the braking torque, which means that
during braking the brake resistor must be able to
dissipate the energy input. The figure shows the re-
lation between mean power and peak power.
■
Calculation of peak power of brake resistor
P
PEAK, MEC
is the peak power at which the motor
brakes on the motor shaft. It is calculated as follows:
P
P EAK;MEC
= P
MOT OR2
M
BR(%)
100
[W ]
P
peak
is the term describing the braking power that is
applied to the brake resistor when the motor applies
the brakes. P
PEAK
is smaller than P
PEAK, MEC
, as the
power is reduced by the efficiency of the motor and
the frequency converter. The peak effect is calcu-
lated as follows:
P
P EAK
= P
MOT OR2
M
BR(%)2
INV 2
MOT OR
100
[W ]
If you select Danfoss’ recommended braking resistor
(R
REC
), you are certain that the braking resistance
can generate a braking torque of 160% on the motor
shaft.
■
Calculation of mean power on brake resistor
The mean power is determined by the period of the
process, i.e. how long you brake in relation to the
period of the process.
Duty-cycle for braking is calculated as follows:
Duty 0 cycle= T
b2
100
T
p
[%]
T
p
= The process time in seconds.
T
b
= The braking time in seconds.
Danfoss sells brake resistors with variable duty-
cycles up to 40%. For example, with a 10%
duty-cycle, brake resistors can take up P
peak
in 10%
of the process period. The remaining 90% of the pe-
riod time is spent on redirecting surplus heat.
The mean power at 10% duty cycle can be calcu-
lated as follows:
P
avg
= P
peak
10
[W ]
The mean power at 40% duty cycle can be calcu-
lated as follows:
P
avg
= P
peak
2:5
[W ]
These calculations apply to intermittent braking with
period times of up to 120 seconds.
NB!:
Period times longer than 120
sec. may lead to overheating of the resistor.
■
Continuous braking
For continuous braking, a brake resistor should be
selected in which the constant braking power does
not exceed the mean power P
AVG
of the brake resis-
tor.
Please contact your Danfoss supplier for further in-
formation.
MG.04.A1.02 - VLT is a registered Danfoss trade mark
18
















































