Managing the System
Administration
Cisco Small Business NSS300 Series Smart Storage Administration Guide
60
3
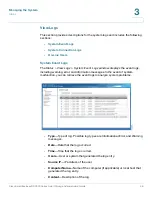
•
Subnet Mask
—Subnet mask of this interface.
•
Gateway
—IP address of the network gateway device.
•
MAC Address
—MAC address of this interface.
•
Speed
—Negotiated or specified link speed.
•
MTU
—Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for this interface.
•
Link
—Status of this interface. A green light indicates that the interface is
active. If only one NIC is used, the web interface will not show the other link
as down or not in use. It will only show both NICs if the NSS is configured as
a standalone from the discovery tool.
•
Edit
—Allows you to turn off DHCP, specify a static IP address, enable the
NAS to be a DHCP server, and allows you to specify link speed or set it to
auto negotiation. When you click
Edit
, the TCP/IP-Property window opens
and the following options are available:
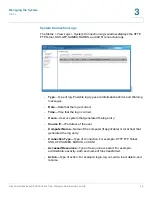
•
Network Speed
—From the drop-down list, select from the following
options:
-
Auto-negotiation
—Allows the server to adjust transfer rates
automatically.
-
1000 Mbps full-duplex
—Sets this transfer rate.
-
100 Mbps full-duplex
—Sets this transfer rate.
•
Obtain IP address settings automatically via DHCP
—Select to enable the
NAS to acquire the IP address from a DHCP server.
•
Use static IP address
—Select to enable the NAS to use a static IP address.
Enter the static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
•
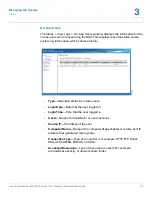
Enable DHCP Server
—If DHCP is not available in the LAN where the NAS is
located, you can enable this function to enable the NAS as a DHCP server
and allocate dynamic IP address to DHCP clients in the LAN.
You can set the range of IP addresses allocated by the DHCP server and the
lease time. Lease time refers to the time that the IP address is leased to the
clients by the DHCP server. When the time expires, the client has to acquire
an IP address again.