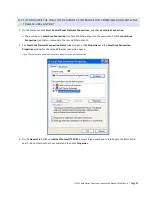
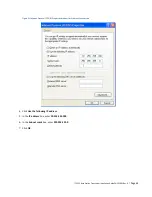
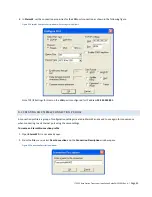
ITC 220 Base Station Transceiver Installation Guide PN 133991 Rev. A
| Page 34
APPENDIX C
— GPS SATELLITE CONSTELLATION OVERVIEW AND ANTENNA PLANNING
CONSIDERATIONS
C.1 GPS SATELLITE CONSTELLATION OVERVIEW
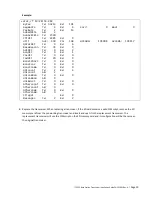
The current GPS satellite constellation is comprised of 30 active satellites in six inclined orbits, with several on-orbit
spares. The GPS satellites operate in circular, approximately 11-hour and 58 minute orbits, at an inclination of 55
degrees at an altitude of 20,200 km.
Figure 15 — GPS satellite constellation
This type of satellite is referred to as an MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) satellite. They are not in geostationary orbit. This is
important because unlike GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit) satellites, which are located at an altitude of 37,790 km over
the equator, MEO satellites move throughout most of the sky, so there is no significantly preferential sky visibility
sector when installing the GPS antennas at the site. The GPS antenna location selection must be optimized for as much
sky visibility as possible in all directions, not just to the South.