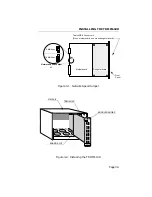
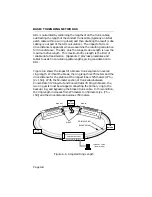
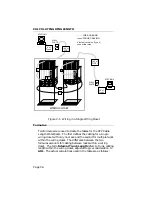
BASIC TOKEN RING NETWORKS
Page A-2
Basic Token Ring Protocol
This summary briefly covers a basic subset of the overall token ring
access protocol. The IEEE Standard 802.5 provides greater detail on
token ring access methods and should be referenced whenever more
complete information is needed.
Each station attached to the ring is identified by a unique station
address differentiating it from all other stations. When a token ring
station is activated and inserted into a ring, several actions are
initiated to maintain order on the ring. All the active stations enter
into a monitor contention dialogue, resulting in one station (the
highest currently active address) establishing itself as the Active
Monitor (AM). As part of its duties, the AM initializes the ring and
transmits a special message frame called a token.
The token circulates around the ring from station to station. Receipt
of the token grants a station the privilege of accessing the ring to
transmit data. When a station receives a token and uses the
opportunity to transmit information, it appears that the token is
removed from the ring and held by the station for the duration of the
transmission. In reality, the token is modified by the station and
used to create the data frame. The token is divided and the
information is inserted between the modified Access Control (AC)
field, and the Ending Delimiter (ED). Figure A-2 shows the token
and information frame formats. Each station receives the token from
a station preceding it on the ring and either uses it while
transmitting data or passes (transmits) it to the next active station on
the ring. When a station has data to transmit, the station modifies
the token AC field, inserts its data into the frame between the AC
and ED, waits for the transmission to circulate completely around the
ring, strips its own data transmission from the ring, and then
restores the token. A Token Holding Timer (THT) controls the length
of time that any station may retain the token. Here is a typical token
ring sequence:
1.
AM initiates the ring and places the token on the ring.
2.
Station xxx wants to send some data to station yyy. Station xxx
modifies the token by inserting the information addressed to
station yyy.