PROFIBUS
BC3150
84
Version: 2.1.0
6.1.4
Plug connectors, cables and switches
The physics of the transmission
Physical aspects of the data transmission are defined in the PROFIBUS standard. See PROFIBUS layer 1
(physical layer).
The types of area where a fieldbus system can be used is largely determined by the choice of the
transmission medium and the physical bus interface. In addition to the requirements for transmission
security, the expense and work involved in acquiring and installing the bus cable is of crucial significance.
The PROFIBUS standard therefore allows for a variety of implementations of the transmission technology
while retaining a uniform bus protocol.
Cable-based transmission: This version, which accords with the American EIA RS-485 standard, was
specified as a basic version for applications in production engineering, building management and drive
technology. A twisted copper cable with one pair of conductors is used. Depending on the intended
application area (EMC aspects should be considered) the shielding may be omitted.
Cable-related faults
Two types of conductor are available, with differing maximum conductor lengths; see the "RS485" table. The
plug connector assignment and the wiring are shown in the diagram below. Note the special requirements on
the data cable for baud rates greater than 1.5 Mbaud. The correct cable is a basic requirement for correct
operation of the bus system. If a "simple" 1.5 Mbaud cable is used, reflections and excessive attenuation can
lead to some surprising phenomena. This could, for example be that some station is not connected, but
when the neighboring station is unplugged the connection appears again. Or there may be transmission
errors when a specific bit pattern is transmitted. The result of this can be that when the equipment is not
operating, PROFIBUS works without faults, but that there are apparently random bus errors after start-up.
Reducing the baud rate (< 93.75 kbaud) corrects this faulty behavior.
If reducing the baud rate does not correct the error, then in many cases this can indicate a wiring fault. The
two data lines maybe crossed over at one or more connectors, the termination resistors may not be switched
on, or they may be active at the wrong locations.
Note
Preassembled cable from Beckhoff
Installation is made a great deal more straightforward if preassembled cables from Beck-
hoff are used. Wiring errors are avoided, and commissioning is more rapidly completed.
The range includes fieldbus cables, power supply cables, sensor cables and accessories
such as termination resistors and T-pieces. Connectors and cables for field assembly are
nevertheless also available.
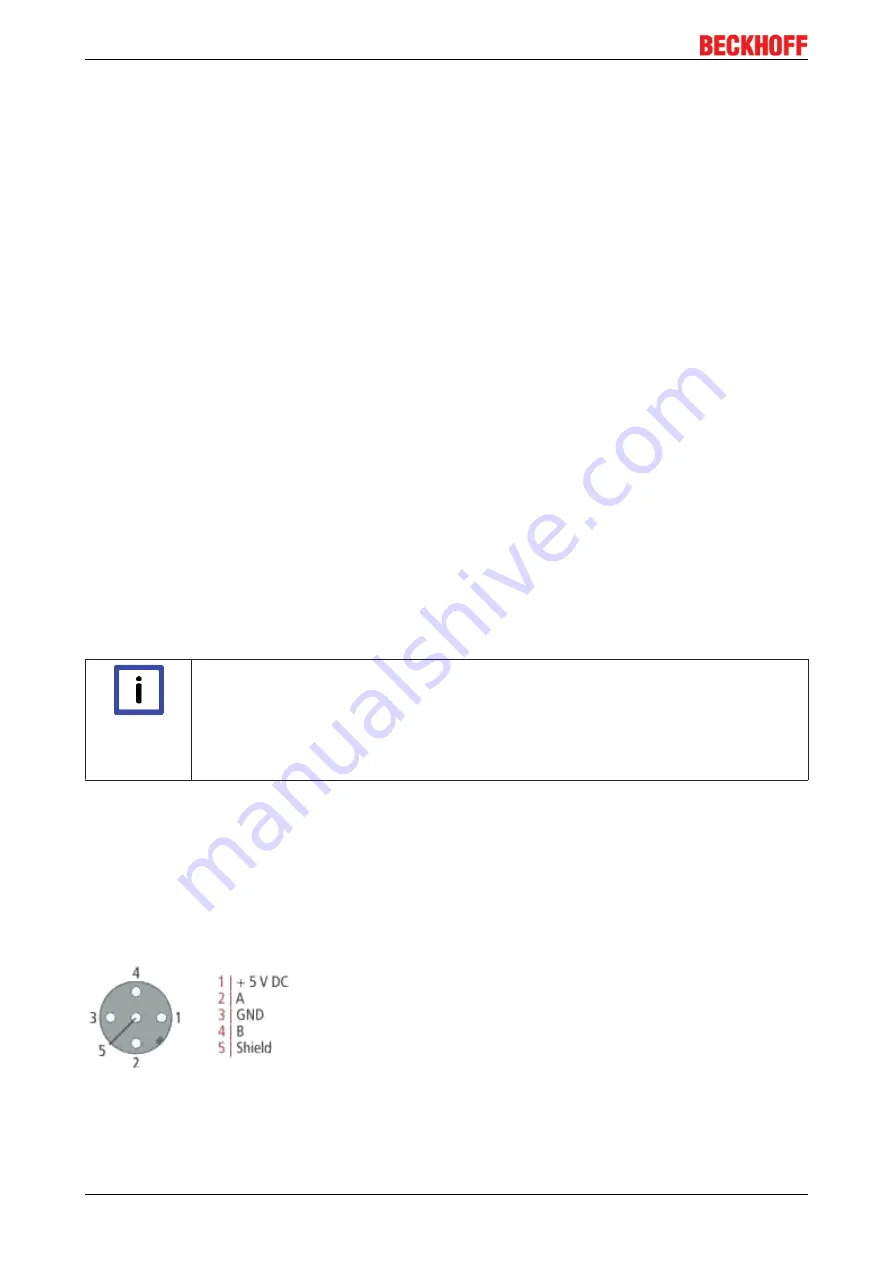
PROFIBUS connection of the Fieldbus Box modules
The M12 socket is inverse-coded and has 5 contact pins. Pin 1 transfers 5 V
DC
, pin 3 transfers GND for the
active termination resistor. These must never be misused for other functions, as this can lead to destruction
of the device. Pins 2 and 4 transfer the PROFIBUS signals. These must never be swapped over, as this will
prevent communication. Pin 5 transfers the shield, which is capacitively connected to the base of the
Fieldbus Box.
PROFIBUS socket pin assignment
Fig. 74: Pin assignment M12 socket
















































