– 160 –
CXD3068Q
§ 5-6. AGCNTL (Automatic Gain Control) Function
The AGCNTL function automatically adjusts the filter internal gain in order to obtain the appropriate servo loop
gain. AGCNTL not only copes with the sensitivity variation of the actuator and photo diode, etc., but also
obtains the optimal gain for each disc.
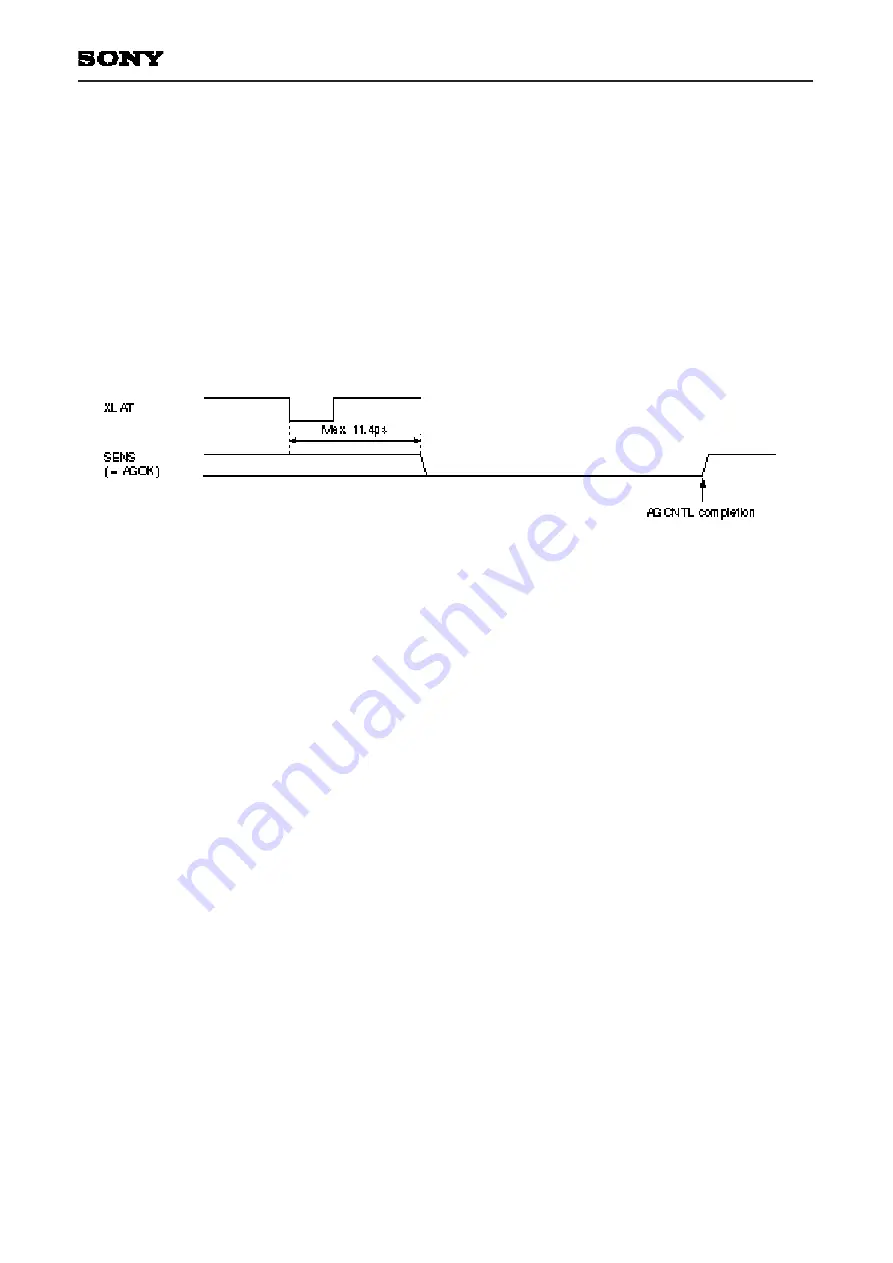
The AGCNTL command is sent when each servo is turned on. During AGCNTL operation, if the upper 8 bits of
the command register are 38 (Hex), the completion of AGCNTL operation can be confirmed by monitoring the
SENS pin. (See Timing Chart 5-4 and "Description of SENS Signals".)
Setting D9 and D8 of $38 to 1 set FCS (focus) and TRK (tracking) respectively to AGCNTL operation.
Note) During AGCNTL operation, each servo filter gain must be normal, and the anti-shock circuit (described
hereafter) must be disabled.
Timing Chart 5-4.
Coefficient K13 changes for AGF (focus AGCNTL) and coefficients K23 and K07 change for AGT (tracking
AGCNTL) due to AGCNTL.
These coefficients change from 01 to 7F (Hex), and they must also be set within this range when written
externally.
After AGCNTL operation has completed, these coefficient values can be confirmed by reading them out from
the SENS pin with the serial readout function (described hereafter).
AGCNTL related settings
The following settings can be changed with $35, $36 and $37.
FG6 to FG0; AGF convergence gain setting, effective setting range: 00 to 57 (Hex)
TG6 to TG0; AGT convergence gain setting, effective setting range: 00 to 57 (Hex)
AGS;
Self-stop on/off
AGJ;
Convergence completion judgment time
AGGF;
Internally generated sine wave amplitude (AGF)
AGGT;
Internally generated sine wave amplitude (AGT)
AGV1;
AGCNTL sensitivity 1 (during rough adjustment)
AGV2;
AGCNTL sensitivity 2 (during fine adjustment)
AGHS;
Rough adjustment on/off
AGHT;
Fine adjustment time
Note) Converging servo loop gain values can be changed with the FG6 to FG0 and TG6 to TG0 setting values. In
addition, these setting values must be within the effective setting range. The default settings aim for 0dB at
1kHz. However, since convergence values vary according to the characteristics of each constituent
element of the servo loop, FG and TG values should be set as necessary.
Summary of Contents for PV420S
Page 1: ...SERVICE MANUAL PV420S WWW BBK RU ...
Page 72: ... 69 CXD3068Q Block Diagram ...
Page 73: ... 70 CXD3068Q Pin Configuration ...
Page 122: ... 119 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 1 3 ...
Page 123: ... 120 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 1 4 ...
Page 124: ... 121 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 1 5 ...
Page 129: ... 126 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 2 1 ...
Page 130: ... 127 CXD3068Q Block Diagram 2 2 ...
Page 131: ... 128 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 2 3 ...
Page 134: ... 131 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 2 6 ...
Page 138: ... 135 CXD3068Q VCO C Mode Fig 3 3 Access Flow Chart Using VCO Control ...
Page 140: ... 137 CXD3068Q Block Diagram 4 1 ...
Page 143: ... 140 CXD3068Q Timing Chart 4 4 ...
Page 147: ... 144 CXD3068Q Fig 4 6 a Auto Focus Flow Chart Fig 4 6 b Auto Focus Timing Chart ...
Page 148: ... 145 CXD3068Q Fig 4 7 a 1 Track Jump Flow Chart Fig 4 7 b 1 Track Jump Timing Chart ...
Page 149: ... 146 CXD3068Q Fig 4 8 a 10 Track Jump Flow Chart Fig 4 8 b 10 Track Jump Timing Chart ...
Page 150: ... 147 CXD3068Q Fig 4 9 a 2N Track Jump Flow Chart Fig 4 9 b 2N Track Jump Timing Chart ...
Page 151: ... 148 CXD3068Q Fig 4 10 a Fine Search Flow Chart Fig 4 10 b Fine Search Timing Chart ...
Page 152: ... 149 CXD3068Q Fig 4 11 a M Track Move Flow Chart Fig 4 11 b M Track Move Timing Chart ...
Page 157: ... 154 CXD3068Q Fig 4 15 CD TEXT Data Timing Chart ...
Page 162: ... 159 CXD3068Q Fig 5 3a Fig 5 3b ...
Page 196: ... 193 CXD3068Q Description of Data Readout ...
Page 200: ... 197 CXD3068Q ...
Page 201: ... 198 CXD3068Q ...
Page 202: ... 199 CXD3068Q ...
Page 207: ... 204 CXD3068Q Package Outline Unit mm ...
Page 208: ...This data sheet has been made from recycled paper to help protect the environment 205 ...
















































