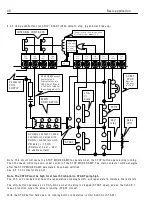
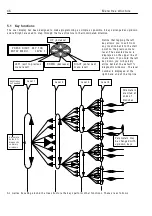
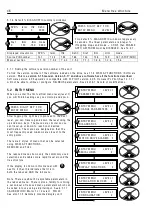
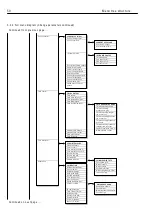
3 6
Bas
i
c app
li
cat
i
on
Answ
e
r
.
2) Mak
i
ng current. If the PL/X has been
i
nstructed to start mak
i
ng current, but the ma
i
n contactor
has not yet c
l
osed, then the motor w
ill
not be ab
l
e to rotate. Th
i
s w
ill
cause the PL/X to phase further
forw ard
i
n an attempt to produced the des
i
red speed. If the contactor then c
l
oses
i
t w
ill
present a stat
i
onary
motor armature on a fu
ll
y phased forw ard stack, stra
i
ght on to the supp
l
y, produc
i
ng destruct
i
ve current. A
ll
th
i
s w
ill
occur
i
n a fe w cyc
l
es of current w h
i
ch
i
s far too fast for the speed
l
oss a
l
arms to operate.
So
l
ut
i
on.
1) Insert an aux
ili
ary norma
ll
y open contact on the ma
i
n contactor
i
n ser
i
es w
i
th the RUN
i
nput on T 3 1.
2) A
l
ternat
i
ve
l
y use contactor w
i
r
i
ng method sho w n
i
n 4.3.2.
Qu
e
st
i
on
. P
l
enty of systems do not appear to suffer from fa
il
ures due to open
i
ng the contactor
i
ncorrect
l
y so
w hy
i
s
i
t so
i
mportant?
Answ
e
r
. If the armature current
i
s d
i
scont
i
nuous, w h
i
ch
i
s very common, then there
i
s much
l
ess stored
i
nduct
i
ve energy and the current a
l
so goes to zero every current cyc
l
e. Th
i
s makes
i
t h
i
gh
l
y un
li
ke
l
y that a
destruct
i
ve s
i
tuat
i
on occurs. The h
i
gh r
i
sk s
i
tuat
i
ons are regenerat
i
ve app
li
cat
i
ons and cont
i
nuous current
modes. Even
i
n these cases
i
t does not a
l
w ays resu
l
t
i
n a destruct
i
ve sequence.
Qu
e
st
i
on
. Even
i
f the contactor operates accord
i
ng to the recommendat
i
ons ho w
i
s protect
i
on afforded
i
f the
contactor co
il
supp
l
y
i
s
l
ost.
Answ
e
r
. Th
i
s
i
s a d
i
ff
i
cu
l
t prob
l
em to so
l
ve us
i
ng e
l
ectron
i
cs. The on
l
y re
li
ab
l
e
i
nsurance
i
s to
i
nsert a D C
sem
i
conductur fuse
i
n the armature c
i
rcu
i
t. Th
i
s fuse shou
l
d open before the thyr
i
stor
j
unct
i
on fa
il
s.
Qu
e
st
i
on
. W hat
i
f the gr
i
d system fa
il
s tota
ll
y?
Answ
e
r
.
Th
i
s
i
s not as bad as
l
os
i
ng the contactor co
il
supp
l
y. Most
i
nsta
ll
at
i
ons natura
ll
y have other
l
oads
that prov
i
de a safe d
i
scharge path before the contactor opens.
Qu
e
st
i
on
. W hat
i
f the gr
i
d system fa
il
s for a fe w cyc
l
es? (Bro w n outs)
Answ
e
r
. The PL/X
i
s des
i
gned to r
i
de through these k
i
nds of supp
l
y d
i
ps. A s soon as
i
t
l
oses synchron
i
sat
i
on
the armature current
i
s quenched. The armature vo
l
tage
i
s then mon
i
tored so that w hen the supp
l
y returns
the PL/X p
i
cks up
i
nto the rotat
i
ng
l
oad at the correct speed.
Qu
e
st
i
on
. W hat other sorts of prob
l
ems occur?
Answ
e
r
. Most prob
l
ems occur w hen users are retro-f
i
tt
i
ng the PL/X
i
nto an ex
i
st
i
ng system. Somet
i
mes these
systems have prev
i
ous
l
y contro
ll
ed the contactor v
i
a a PLC or Dr
i
ve hea
l
thy re
l
ay. These contro
l
systems
may not be
i
nterfaced correct
l
y w
i
th PL/X and s
i
tuat
i
ons occur that drop out the contactor too qu
i
ck
l
y, or
br
i
ng
i
t
i
n too
l
ate.
A nother common prob
l
em
i
s that the contactor
i
s contro
ll
ed correct
l
y for norma
l
runn
i
ng but
i
ncorrect
l
y
dur
i
ng
j
ogg
i
ng or emergency stopp
i
ng.
A nother
i
nstance
i
s the
i
nsta
ll
at
i
on
i
s des
i
gned correct
l
y but the comm
i
ss
i
on
i
ng eng
i
neer uses a
l
oca
l
op
stat
i
on to get each PL/X go
i
ng, that has an
i
n bu
il
t contro
l
prob
l
em.
Summ
a
r
y
.
Us
e
th
e
PL
/X to
c
ont
r
o
l
th
e
m
a
i
n
c
ont
ac
to
r
fo
r
STO
P
, STA
R
T,
j
ogg
i
ng
a
nd
e
m
e
r
g
e
n
c
y stop. A
ll
s
e
qu
e
n
c
i
ng o
cc
u
r
s
a
utom
a
t
i
ca
ll
y. F
i
t s
e
m
i
c
ondu
c
to
r
fus
e
s
i
n th
e
AC supp
l
y
a
nd
a
r
m
a
tu
r
e
c
ir
c
u
i
ts.
Th
e
c
ost of
a
fus
e
i
s m
a
r
g
i
n
a
l
c
omp
a
r
e
d to th
e
c
ost of
r
e
p
a
iri
ng
a
d
a
m
a
g
e
d d
ri
v
e
a
nd suff
e
ri
ng m
ac
h
i
n
e
downt
i
m
e
a
nd
e
ng
i
n
ee
r
ca
ll
out
c
osts.
Summary of Contents for PLX
Page 2: ...2 Contents ...
Page 202: ......