32
ANET1553
Users
Manual
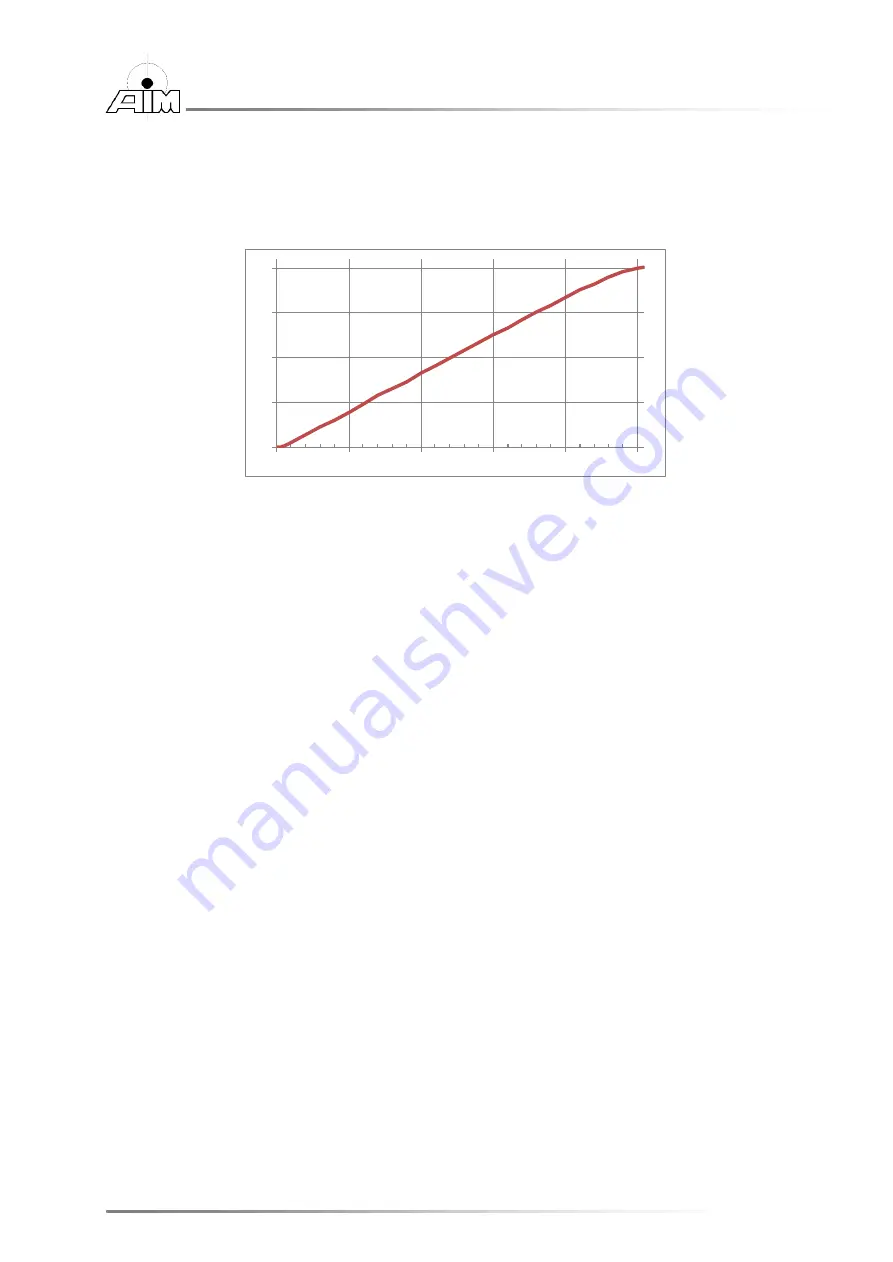
The following figure shows the MILBus output amplitude (on a 70
Ω Bus Termination)
over the different amplitude settings. The Amplitude can be controlled by the user via
the Software API Function (ApiCmd
….).
Figure 4-3 Diagram MILBus output amplitude versus amplitude settings
The X-Axis (
→) is the setting of the voltage (0…255), whereas the Y-Axis (↑) is the
voltage amplitude [V
PP
] of the MILBus (0…20V
PP
). This are typical values, the exact
settings might differ.
4.5 ASP Section
The low power onboard Application Support Processor (ASP) is based on a
System-On-Chip (SOC) hardware and running under an embedded LINUX Operating
System. The SOC hardware offers a built-in Ethernet interface, which is used for the
implementation of the host connection via a Standard Ethernet RJ-45 connector.
Furthermore, the also SOC built-in USB interface has been made available to the user
for mounting external mass data storage devices or e.g. a WLAN stick for wireless.
4.6 Discrete I/Os
The ANET1553 module provides eight user programmable Discrete-I/O signals.
The Discrete I/Os are always operating as an Input . The Output mode of the Discrete
I/Os can be explicitly enabled/disabled by the user via a corresponding Software API
Command (ApiCmd……). Read carefully the following text and figures to avoid any
damage.
An open collector circuitry is used for the discrete output with 4V provided by default by
a pull up resistor (see the following figures).
An external voltage from 0 to 35V can be supplied externally for switching higher
voltages.
Be aware that a series resistor must be provided when a user voltage is used.
This serial resistor must limit the current through the open collector transistor to max.
50 mA. Otherwise the open collector transistor can be damaged.
EMC aspects are covered by filter circuitry.
0
5
10
15
20
0
50
100
150
200
250
















































